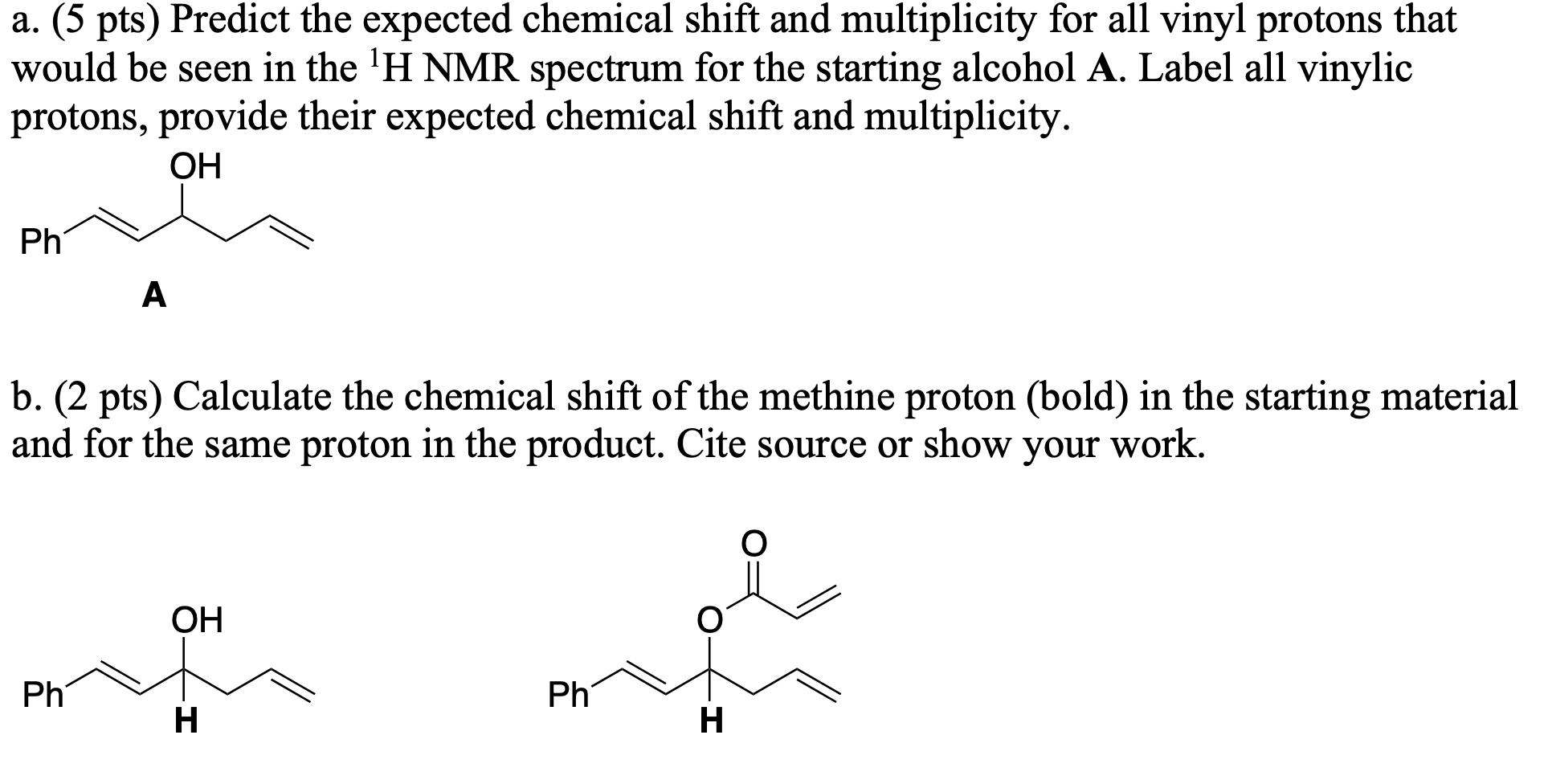
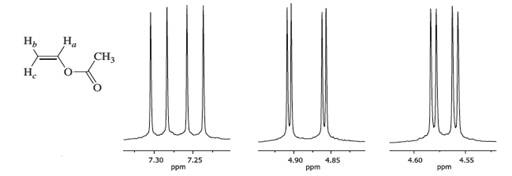
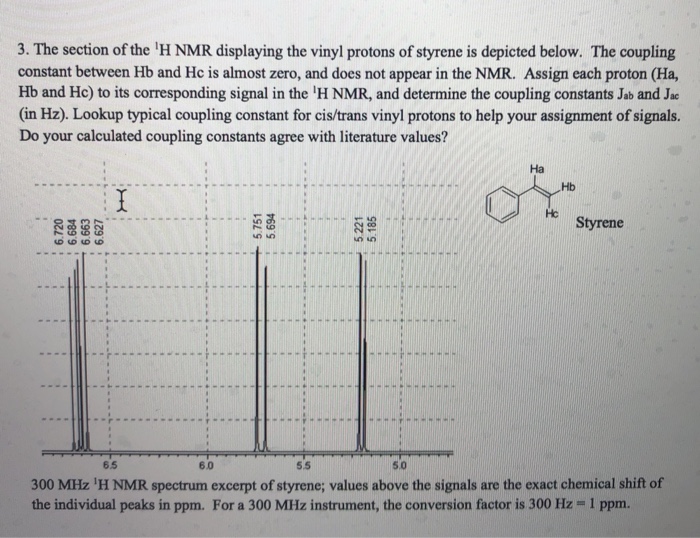
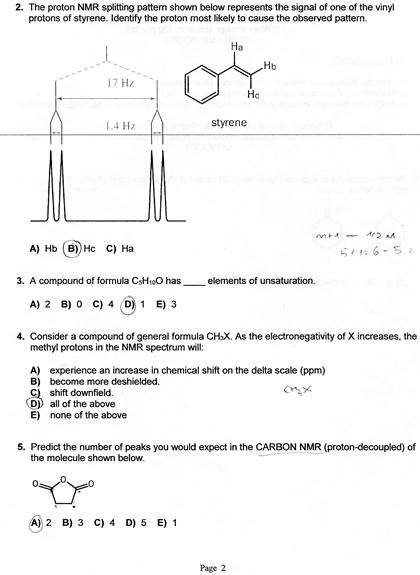
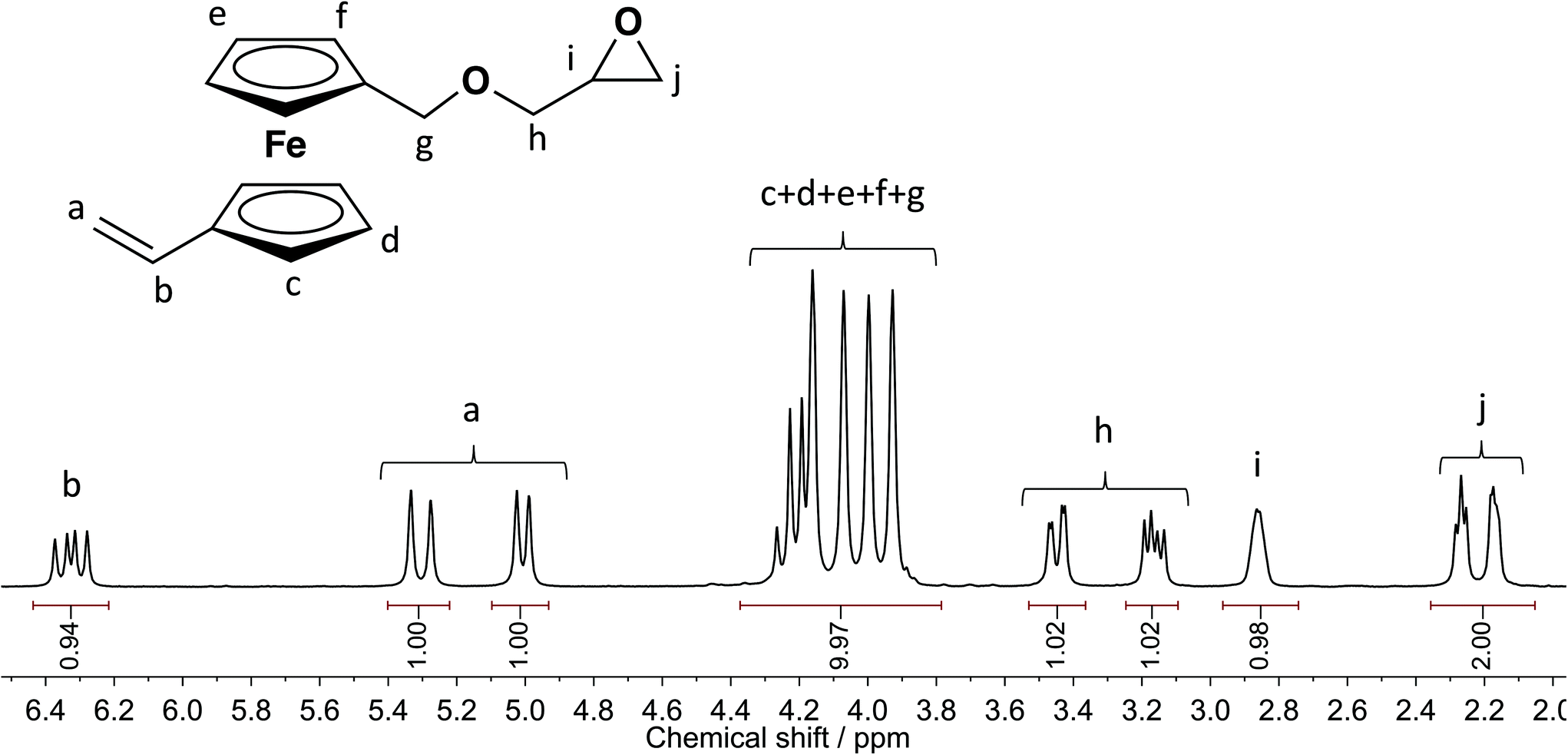
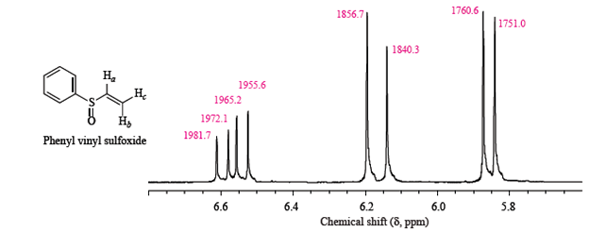
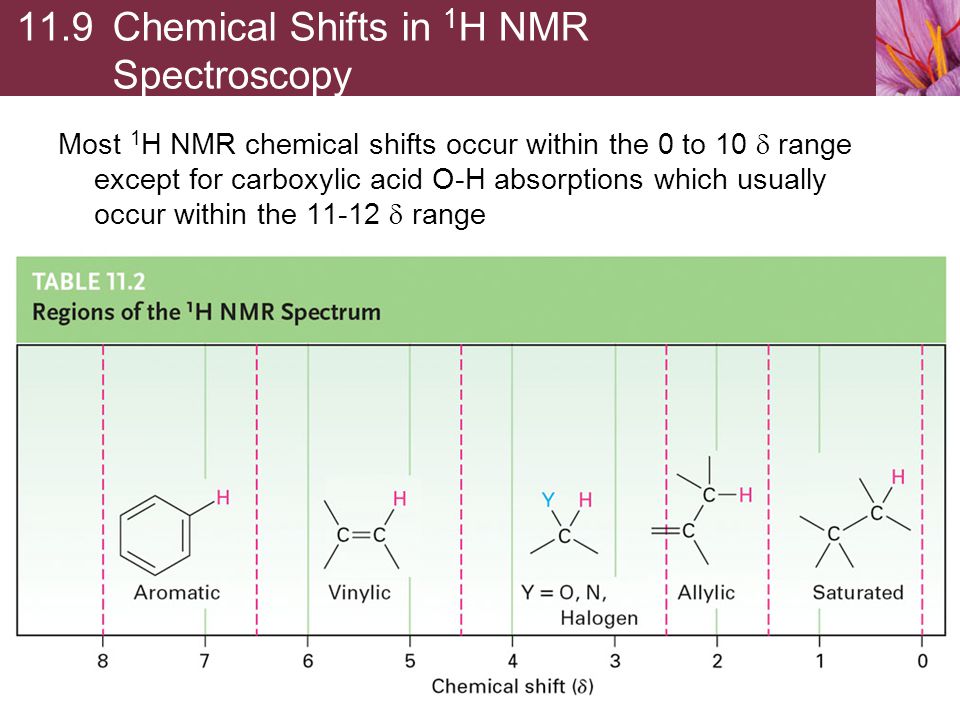
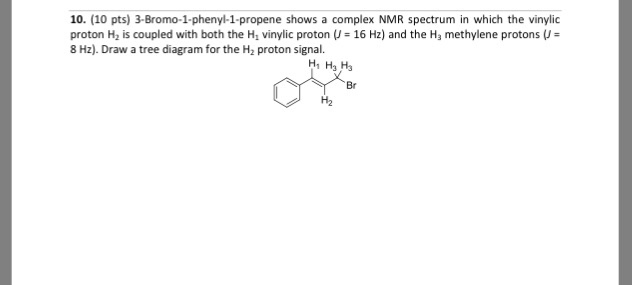
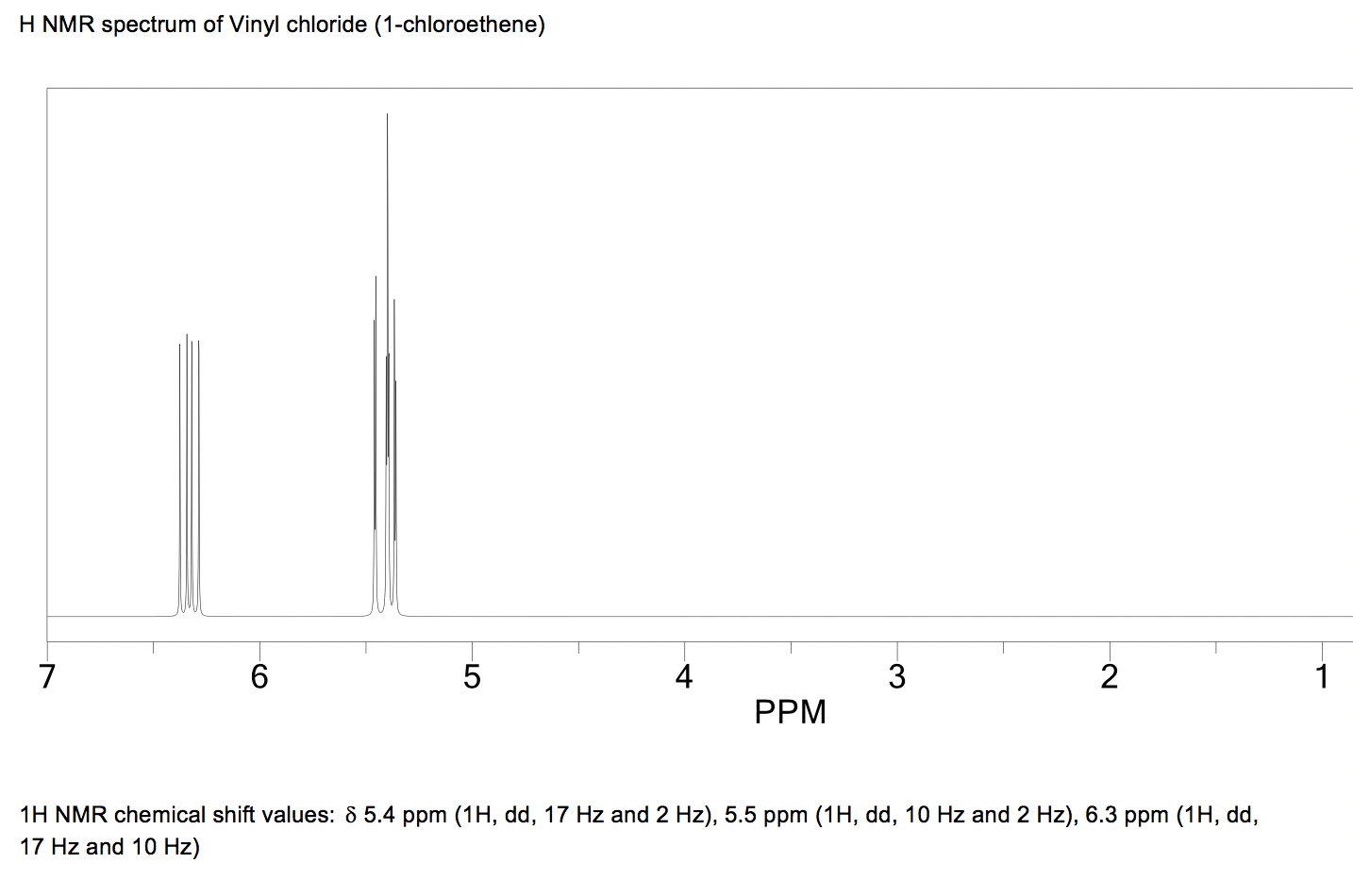
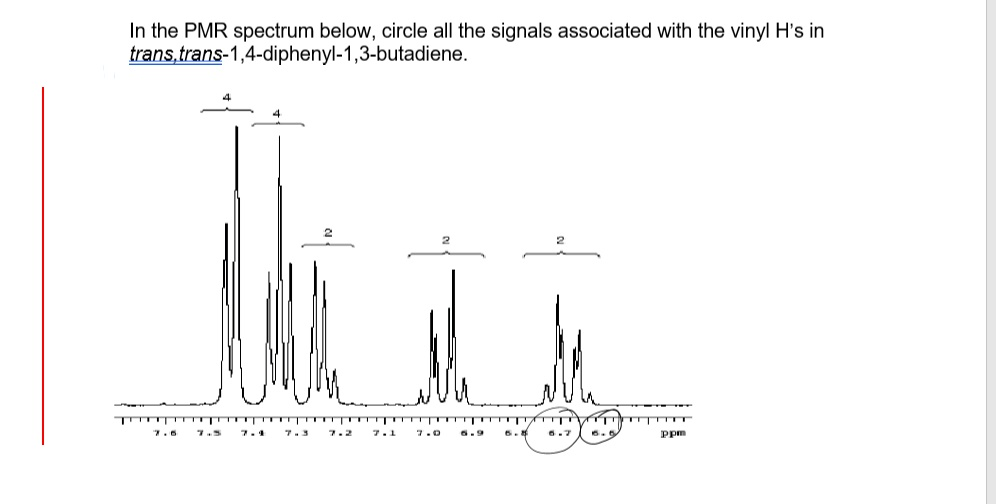
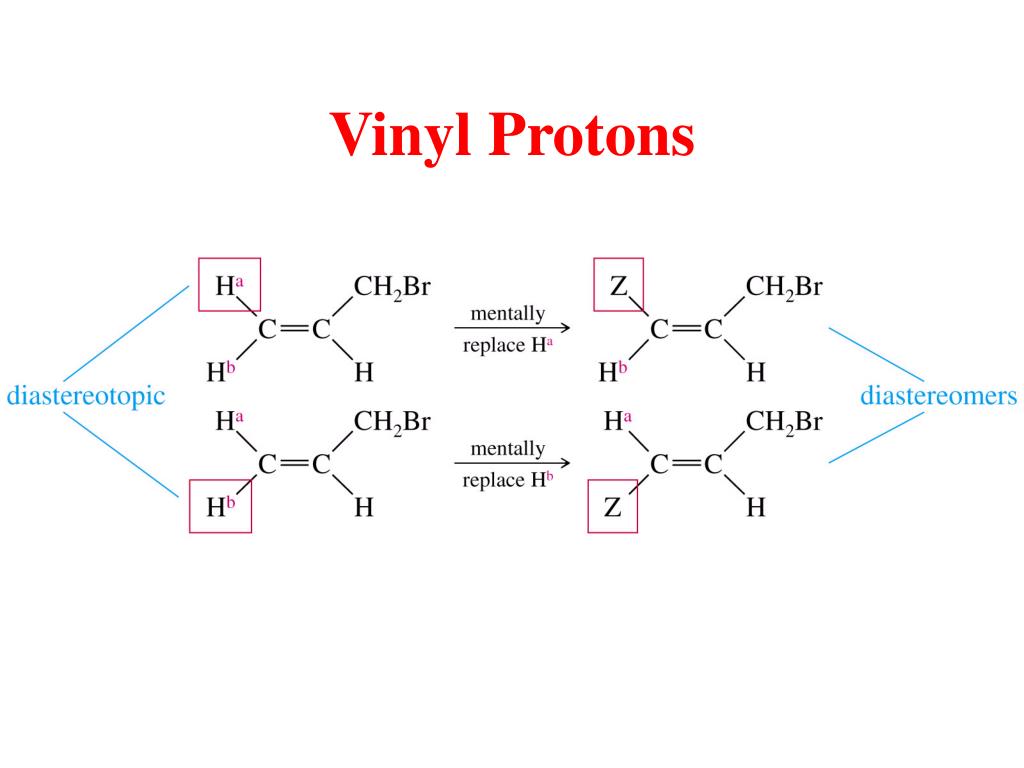
Vinylic Protons Nmr
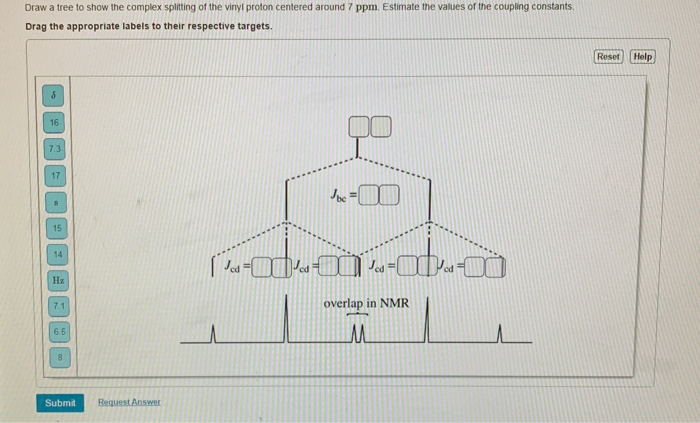
The induced field therefore augments the local field at the vinylic protons.
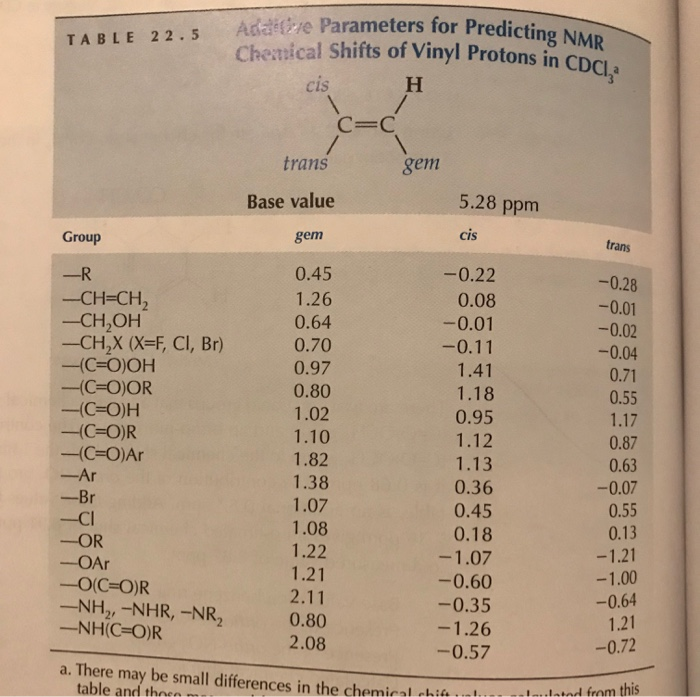
Vinylic protons nmr. As a result the vinylic protons are subjected to a greater local field. 0 at the vinylic protons. 1 h nmr chemical shifts. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance proton nmr hydrogen 1 nmr or 1 h nmr is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in nmr spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen 1 nuclei within the molecules of a substance in order to determine the structure of its molecules.
In fact the 1 h nmr spectra of most organic molecules contain proton signals that are split into two or more sub peaks. Tetramethylsilan tms ch 3 4 si is generally used for standard to determine chemical shift of compounds. We know that a proton alpha to a carbonyl group is pulled downfield. In samples where natural hydrogen h is used practically all the hydrogen consists of the isotope 1 h hydrogen 1.
Consequently their nmr absorptions occur at relatively high chemical shift. Chemical shift is associated with the larmor frequency of a nuclear spin to its chemical environment. The source of spin spin coupling. This is not surprising since the proton is not only vinylic but it is also alpha to a carbonyl group.
In other words frequencies for chemicals are measured for a 1 h or 13 c nucleus of a sample from the 1 h or 13 c resonance of tms. Notice that the proton closest to the carbonyl group is at a higher chemical shift than the proton in cyclohexene 6 05 ppm for cyclohexenone vs.