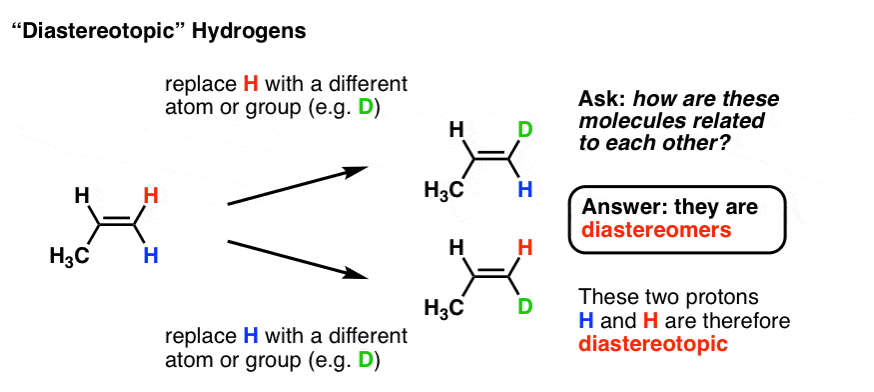
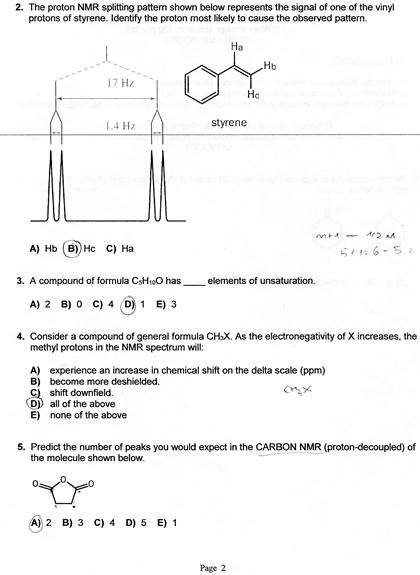
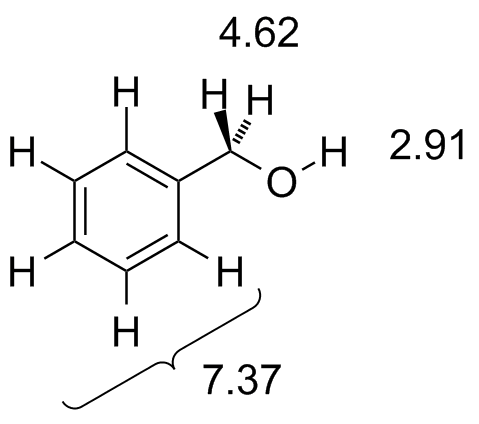
Vinylic Protons Chemical Shift

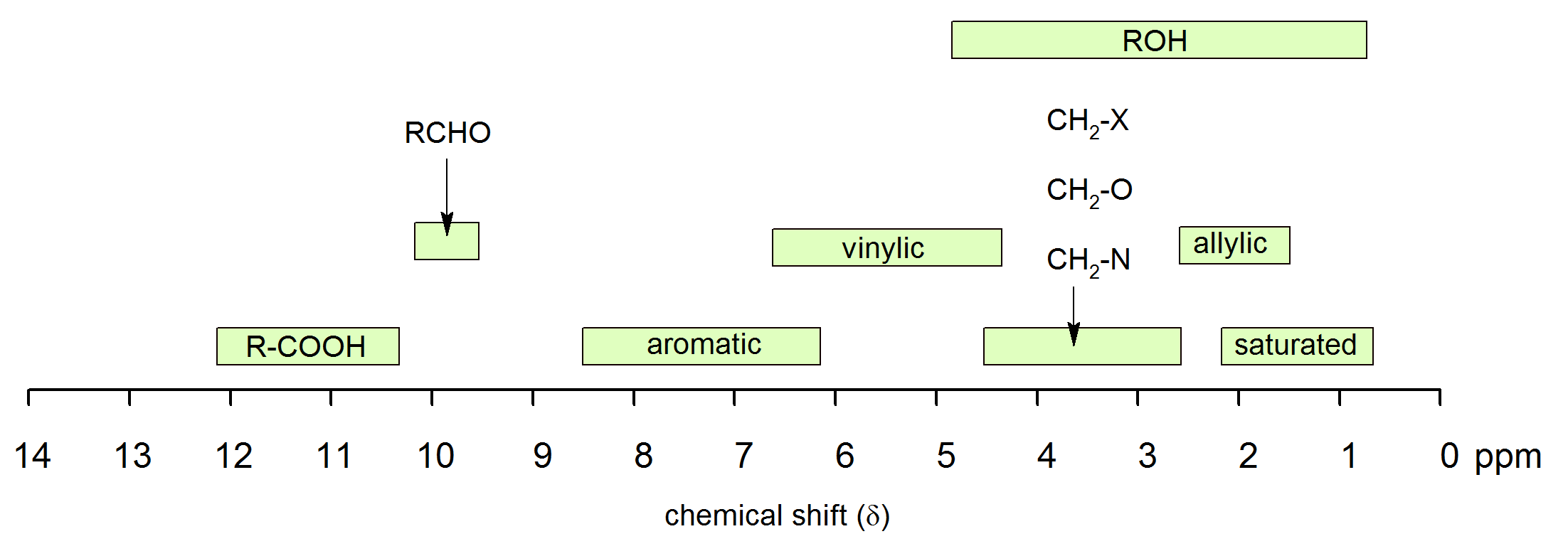
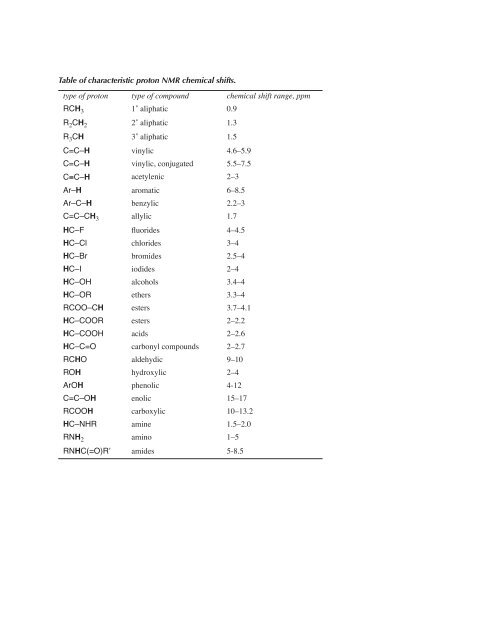
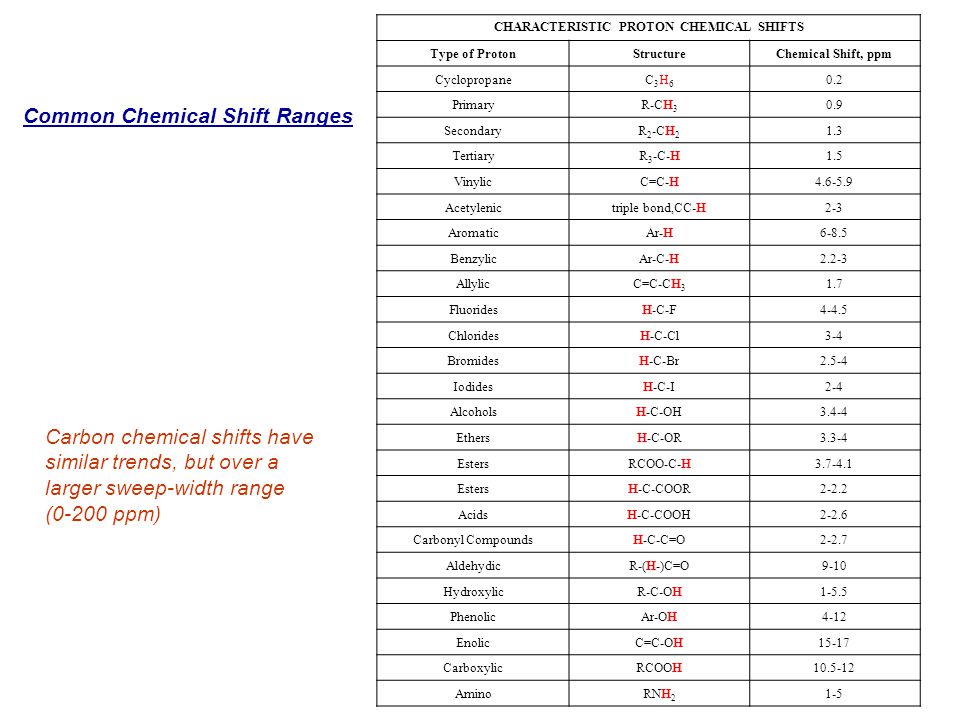
Table of characteristic proton nmr chemical shifts.
Vinylic protons chemical shift. Type of proton type of compound chemical shift range ppm rc h 3 1 aliphatic 0 9 r 2 c h 2 2 aliphatic 1 3 r 3 c h 3 aliphatic 1 5 c c h vinylic 4 6 5 9 c c h vinylic conjugated 5 5 7 5 c. Chemical shift d type of proton examples chemical shift in ppm comments. Table of characteristic proton nmr shifts type of proton type of compound chemical shift range ppm rch 3 1 aliphatic 0 9 r 2 ch 2 2 aliphatic 1 3 r 3 ch 3 aliphatic 1 5 c c h vinylic 4 6 5 9 c c h vinylic conjugated 5 5 7 5 c c h acetylenic 2 3 ar h aromatic 6 8 5 ar c h benzylic 2 2 3 c c ch 3 allylic 1 7 hc f. However this particular orientation makes such a large contribution that it dominates the chemical shift.
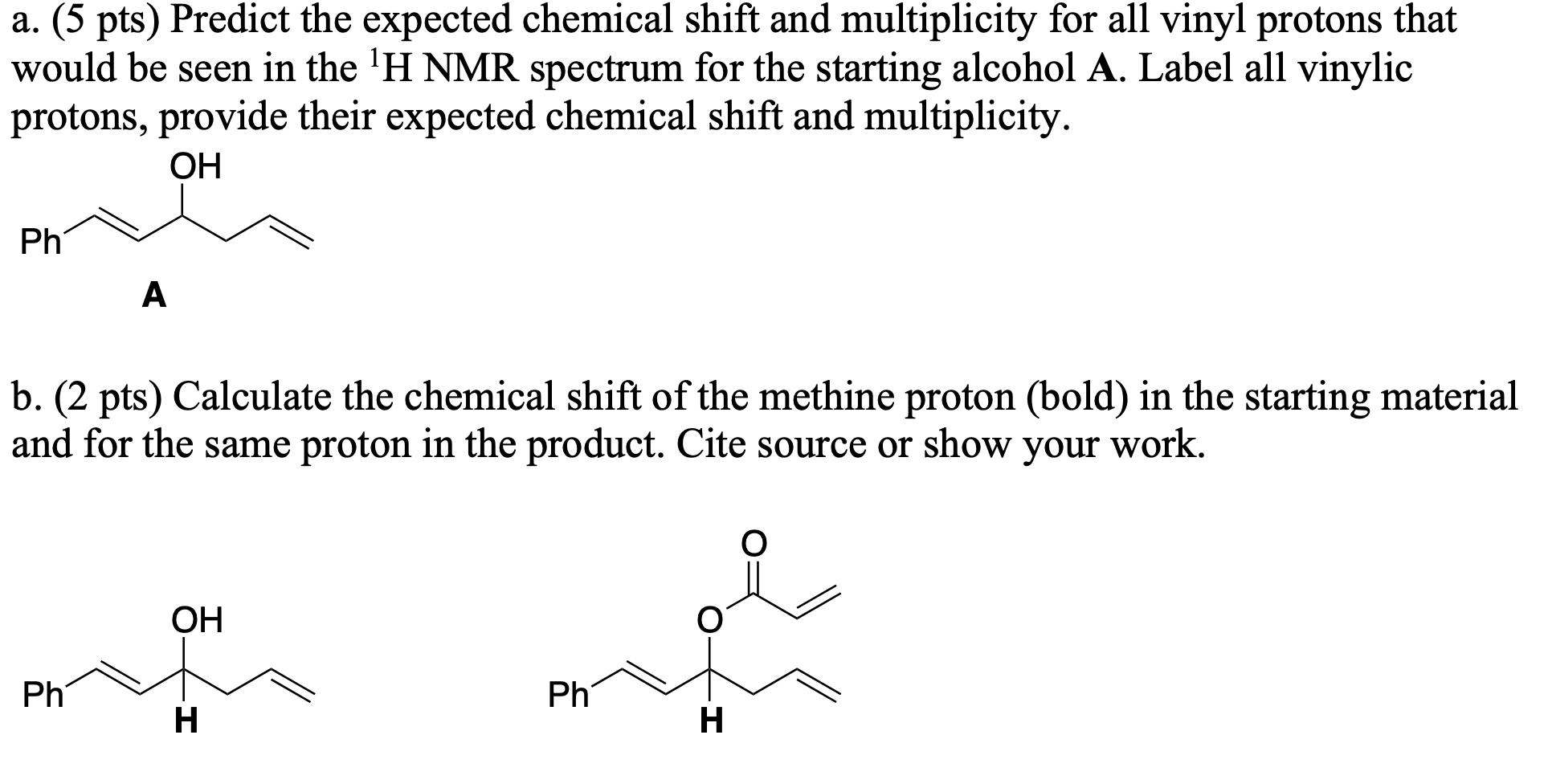
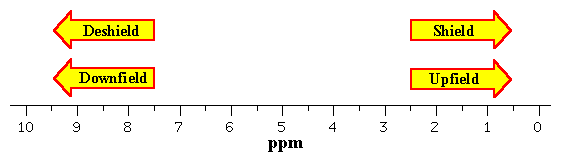
The chemical shift of a vinylic proton is an average over all orientations of the molecule. Notice that the proton closest to the carbonyl group is at a higher chemical shift than the proton in cyclohexene 6 05 ppm for cyclohexenone vs. Chemical shift is associated with the larmor frequency of a nuclear spin to its chemical environment. Some protons resonate much further downfield than can be accounted for simply by the deshielding effect of nearby electronegative atoms.
The chemical shift of protons connected to heteroatoms the second group of protons giving signal in this region is the ones bonded to heteroatoms such as oxygen and nitrogen. Chemical shift is associated with the larmor frequency of a nuclear spin to its chemical environment. This is a general trend add approximately 0 2 0 4 ppm for each additional alkyl group. This is not surprising since the proton is not only vinylic but it is also alpha to a carbonyl group.
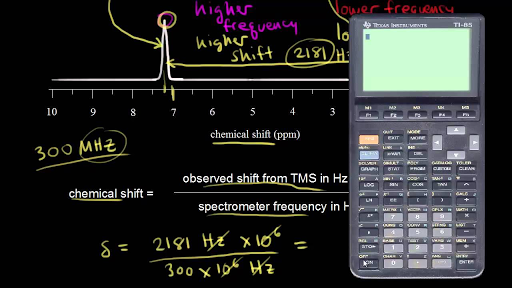
In other words frequencies for chemicals are measured for a 1 h or 13 c nucleus of a sample from the 1 h or 13 c resonance of tms. Table 13 3 typical values of chemical shifts type of proton approximate 8 type of proton approximates 0 9 alkane ch methyl alkane ch methylene 1 7 1 3 c c ch ph h aromatic ph ch benzylic 7 2 alkane ch 1 4 23 mething le r c aldehyde 9 10 ch methyl ketone 2 1 2 5 cec h. 1 h nmr chemical shifts. 0 8 1 5 ppm alkane c h.
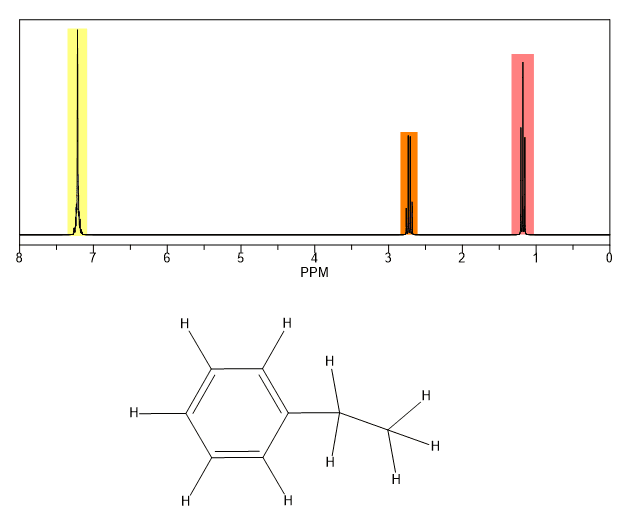
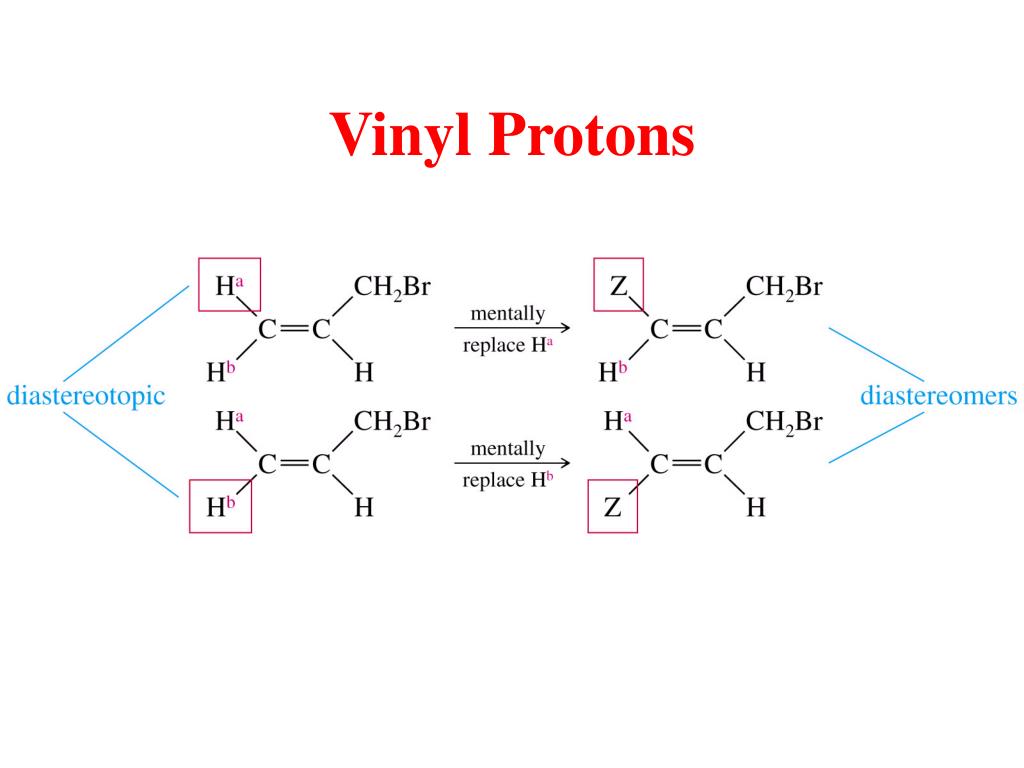
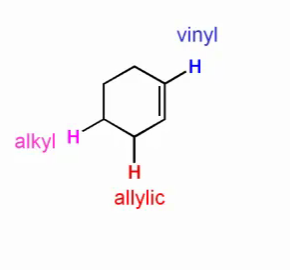
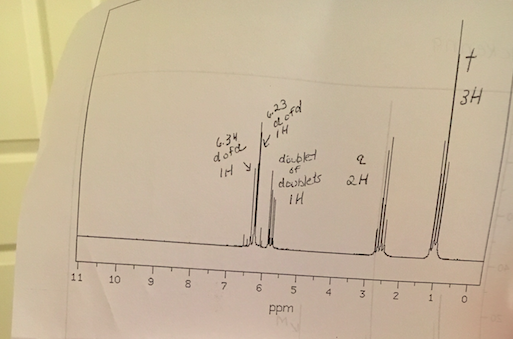
The chemical shifts of aromatic and vinylic protons. Predict the chemical shifts of the protons in the following compounds. Vinylic protons those directly bonded to an alkene carbon and aromatic benzylic protons are dramatic examples. C h acetylenic 2 3 ar h aromatic 6 8 5 ar c h benzylic 2 2 3 c c c h.
We know that a proton alpha to a carbonyl group is pulled downfield. 1 h nmr chemical shifts. The greater the substitution on the carbon bearing the hydrogen the further downfield higher frequency the resonance occurs. In other words frequencies for chemicals are measured for a 1 h or 13 c nucleus of a sample from the 1 h or 13 c resonance of tms.
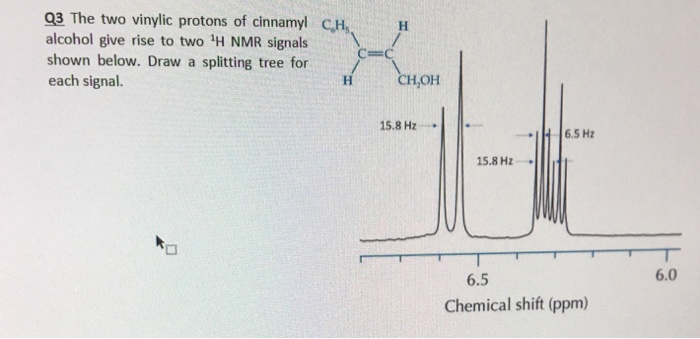
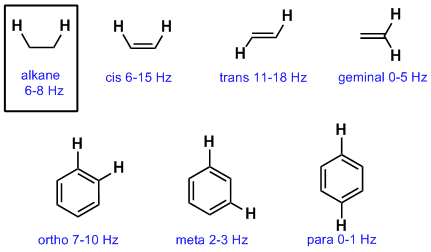
We ll consider the aromatic proton. Splitting between vinylic protons in alkenes depends strongly on the geometrical relation. Tetramethylsilan tms ch 3 4 si is generally used for standard to determine chemical shift of compounds.