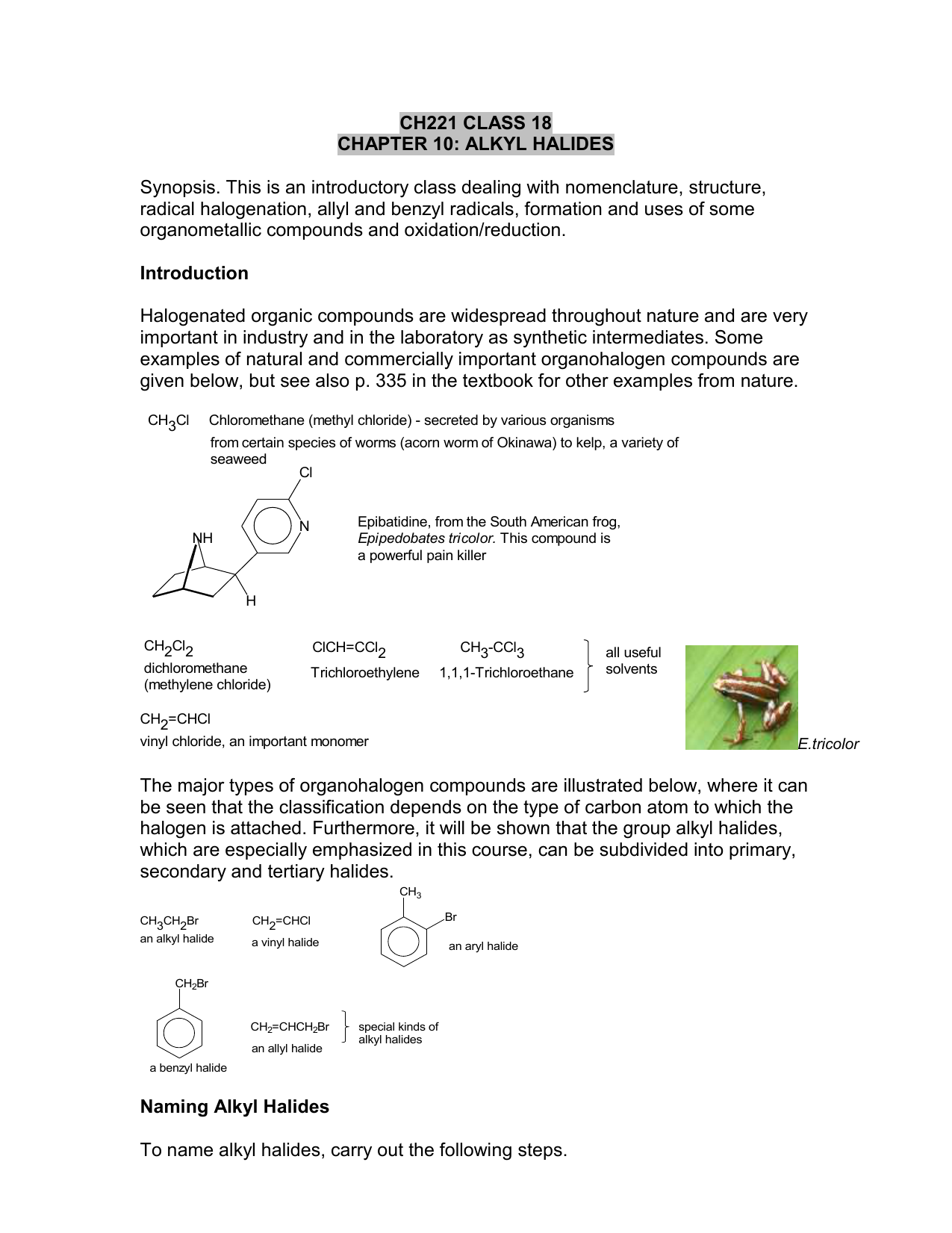
Vinylic Halide Structure

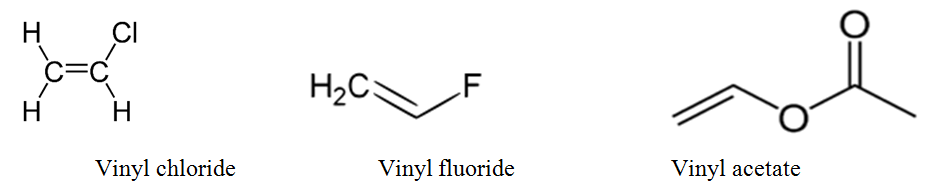
In organic chemistry a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula ch 2 chx x halide.
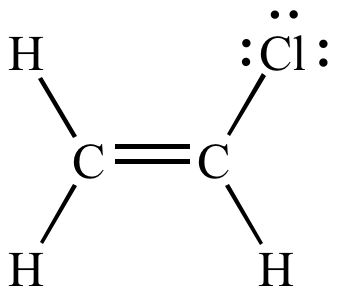
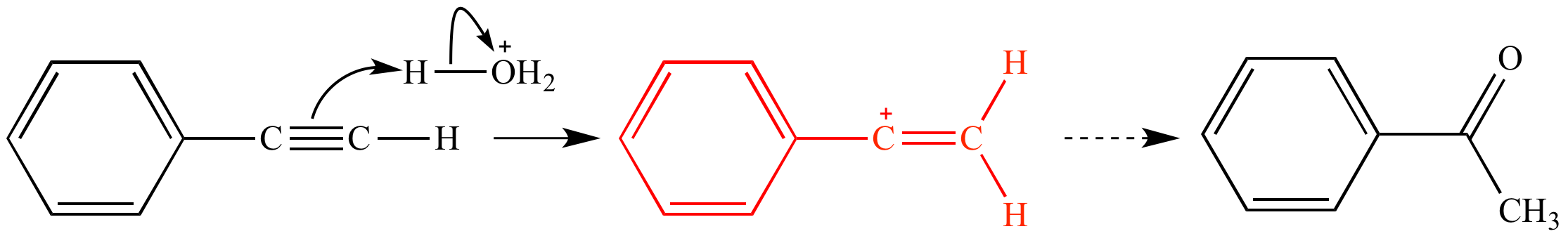
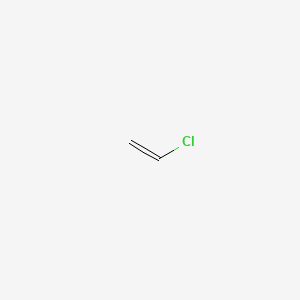
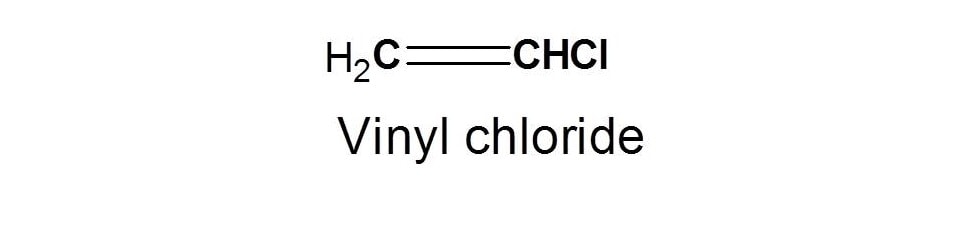
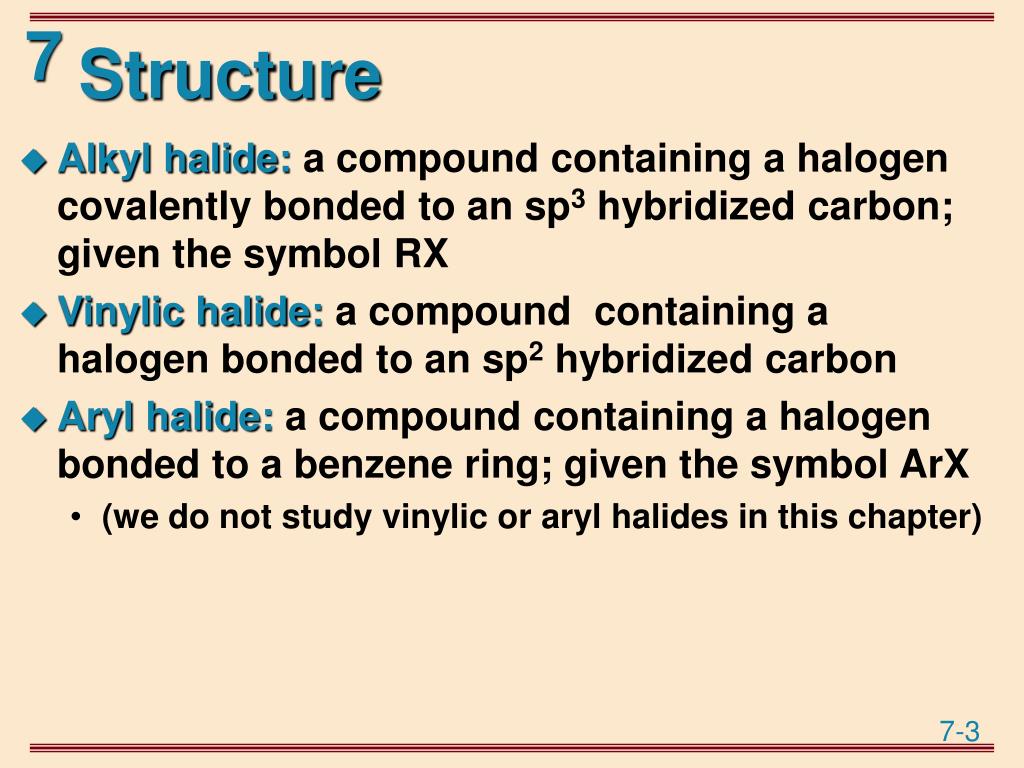
Vinylic halide structure. When a hydrogen halide adds to the carbon carbon triple bond of an alkyne addition of the first molecule is faster than the second and a. An aryl halide has general formula c 6h 5x in which an halide group x has substituted the aryl ring. As we saw in the previous section an aryl halide is classified by its distinct bonding of a halogen directly to a benzene ring. Vinyl chloride h 2c chcl is an example.
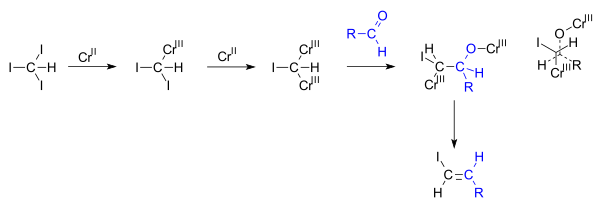
In aryl halides the halogen atom is directly bonded to an sp 2 hybridised carbon of benzene. It is prepared from 1 2 dichloroethane clch 2 ch 2 cl. Addition of a hydrogen halide to an alkyne. Formally this is ethylene h 2c ch 2 with one of the hydrogens substituted by a heteroatom.
General structure of a vinyl halide where x is a halogen and r is a radical group. A vinylic halide from an aryl halide. It contains two sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms and one sp 3 hybridized carbon atom. In other words it is a methylene bridge ch 2 attached to a vinyl group ch ch 2.
The term vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group. For this reason alkenyl halides with the formula rch chx are sometimes called vinyl halides. Its empirical formula is c 2 h 3 more generally a vinylic cation is any disubstituted trivalent carbon where the carbon bearing the positive charge is part of a double bond and is sp hybridized in the chemical literature substituted vinylic cations are often referred to as vinyl cations and understood to. From a structural standpoint one of the.
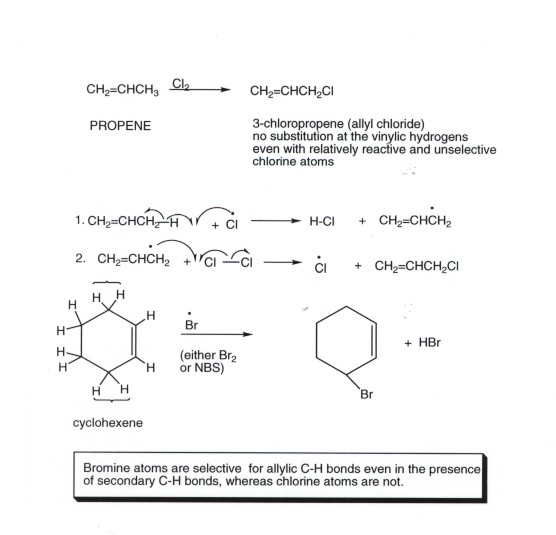
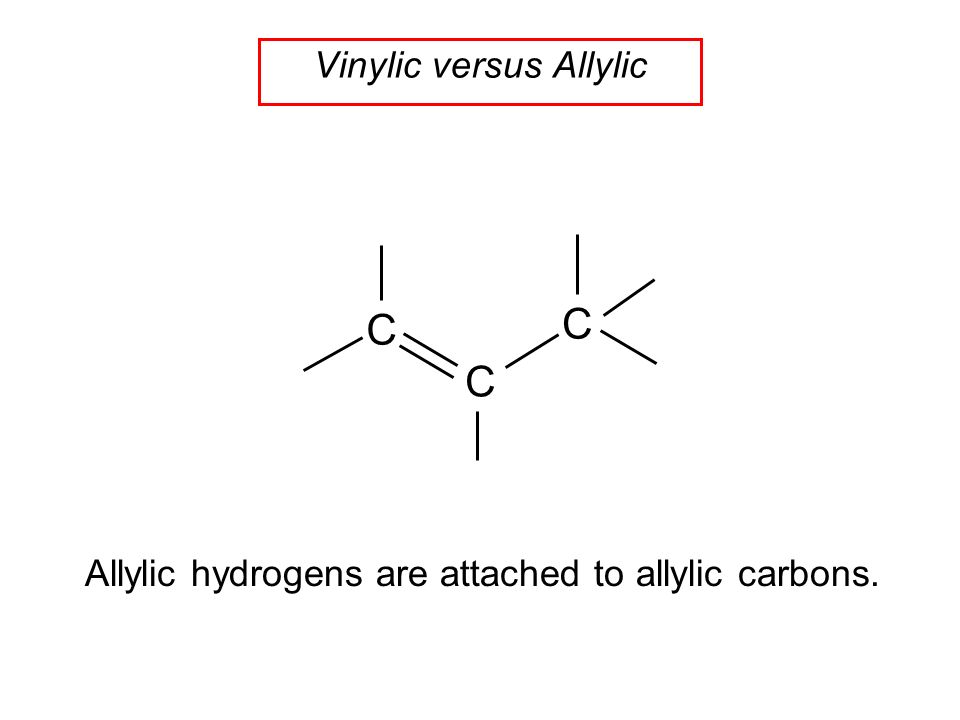
The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon. A vinyl halide is clearly a species with a formula h 2c c x h in which a halide is directly bound to an olefinic bond. The vinyl cation is a carbocation with the positive charge on an alkene carbon. Dehydrohalogenation of a dihalide treatment of a geminal dihalide both halogens on the same carbon or a vicinal dihalide halogens on adjacent carbons with a base such as sodium ethoxide naoch 2 ch 3 yields a vinylic halide.
In chemistry vinyl or ethenyl abbreviated as vi is the functional group with the formula c h ch 2 it is the ethylene iupac ethene molecule h 2 c ch 2 with one fewer hydrogen atom. When one hydrogen atom is removed from the third carbon atom of a propane molecule it is equivalent to an allyl group. The vinylic halide prepared in greatest amount as an industrial chemical is vinyl chloride ch 2 chcl. Aryl halides or haloarenes.
Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule.