Vinylic Carbon Structure
It contains two sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms and one sp 3 hybridized carbon atom.
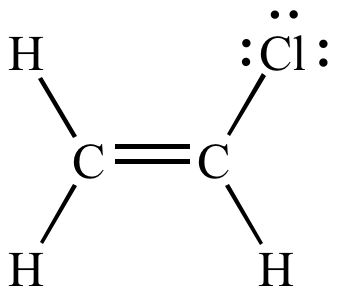
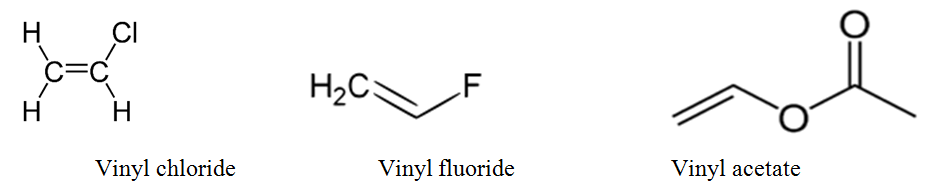
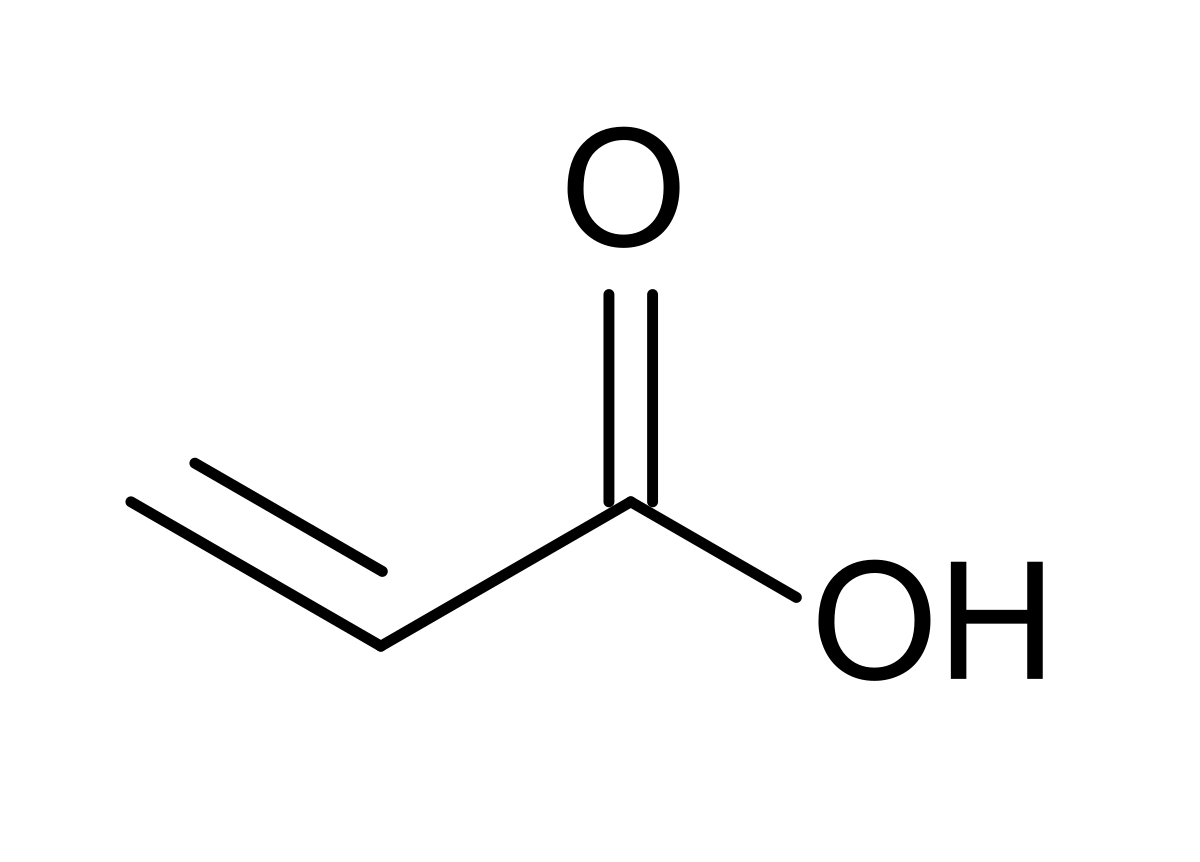
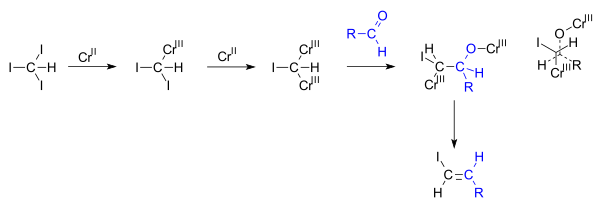
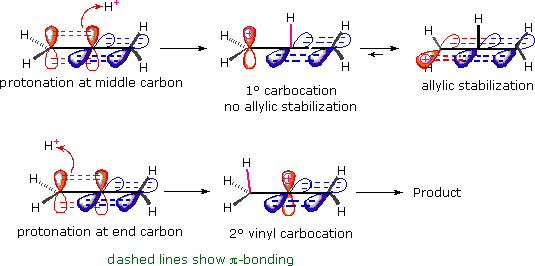
Vinylic carbon structure. In line formulas such as the following a carbon atom is assumed to be at every intersection of two lines and at the end. An industrially important example is vinyl chloride precursor to pvc a plastic. A vinylic carbocation which has an empirical formula of c h is a carbocation that has a positive charge only on the alkene carbon atom. The carbocation carbon has sp hybridization.
Lewis structure of vinyl chloride a vinyl ic halide. A carbocation in which the carbon atom having the open octet and positive formal charge is part of a carbon carbon double bond. The general formula for vinyl group is r ch ch 2 in which both carbon atoms are bonded with double bond and r is attached at vinylic position. Since both carbon atoms form a double covalent bond so both are sp 2 hybridized.
Its empirical formula is c 2 h 3 more generally a vinylic cation is any disubstituted trivalent carbon where the carbon bearing the positive charge is part of a double bond and is sp hybridized in the chemical literature substituted vinylic cations are often referred to as vinyl cations and understood to. This molecule has four vinyl ic positions each marked with. The name is also used for any compound containing that group namely r ch ch 2 where r is any other group of atoms. General vinylic carbocation structure.
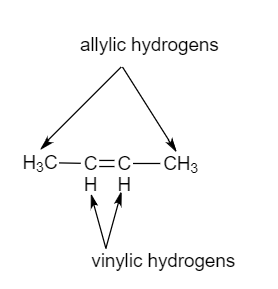
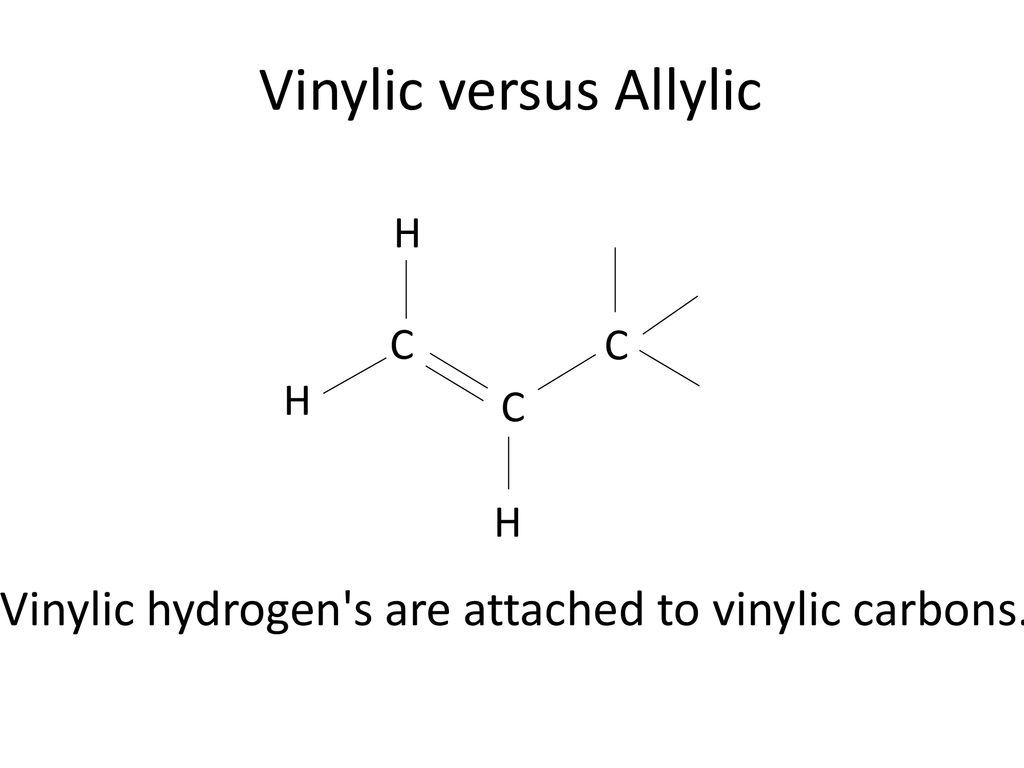
Vinylic chlorides and bromides constitute a diverse class of marine natural products. When one hydrogen atom is removed from the third carbon atom of a propane molecule it is equivalent to an allyl group. On or bonded to the carbon of an alkene. Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule.
Vinylic halides natural occurrence. Any trivalent disubstituted carbon is generally a vinylic carbocation in which the carbon atom which is bearing the positive charge is found to be double bonded and will always exist as sp hybridized. In chemistry vinyl or ethenyl abbreviated as vi is the functional group with the formula c h ch 2 it is the ethylene iupac ethene molecule h 2 c ch 2 with one fewer hydrogen atom. In other words it is a methylene bridge ch 2 attached to a vinyl group ch ch 2.
The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon.