Vinylic Carbon Definition

Vinyl is one of the alkenyl functional groups.
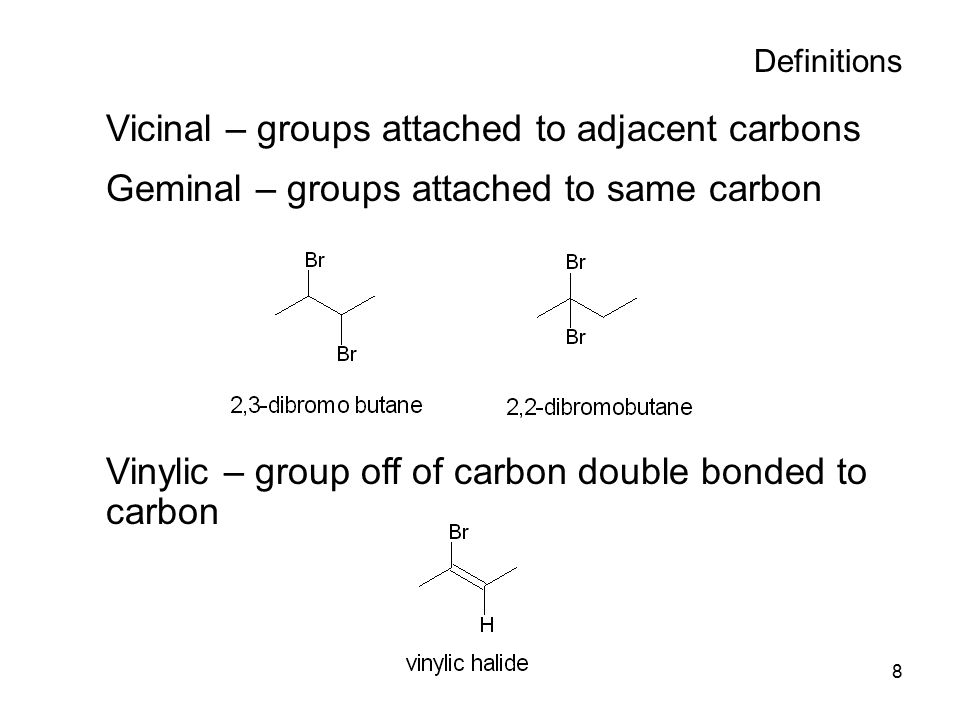
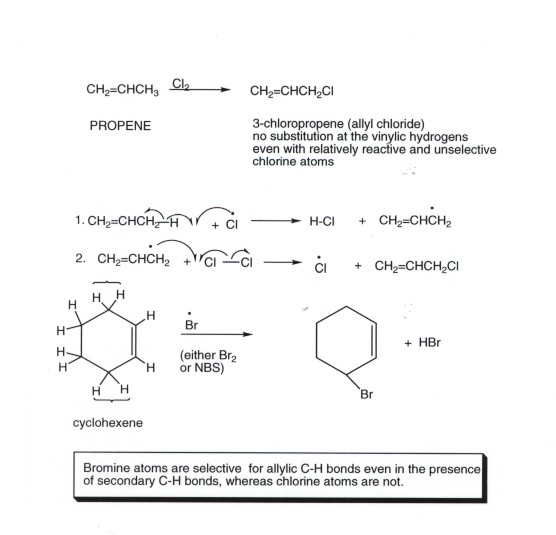
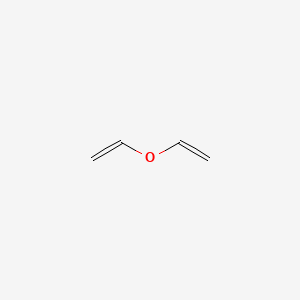
Vinylic carbon definition. On a carbon skeleton sp 2 hybridized carbons or positions are often called vinylic. A styrenic crosslinker with two vinyl groups is called divinyl benzene. The vinyl cation is a carbocation with the positive charge on an alkene carbon. In vinylic halides the carbon that bears the halogen is doubly bonded to another carbon.
In alkyl halides all four bonds to the carbon that bears the halogen are single bonds. Allyls acrylates and styrenics contain vinyl groups. Of or relating to vinyl meaning pronunciation translations and examples. Carbocation stability resonance rearrangement allylic vinylic examples organic chemistry duration.
Any of various compounds containing the vinyl group typically highly reactive. An allylic carbon is an sp3 carbon that is adjacent to a vinylic carbon. In aryl halides the halogen bearing carbon is part of. The organic chemistry tutor 108 416 views 15 37.
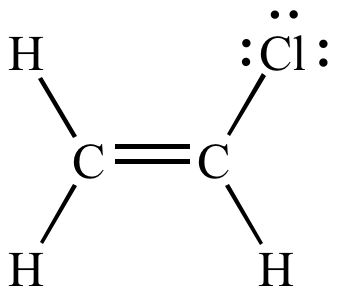
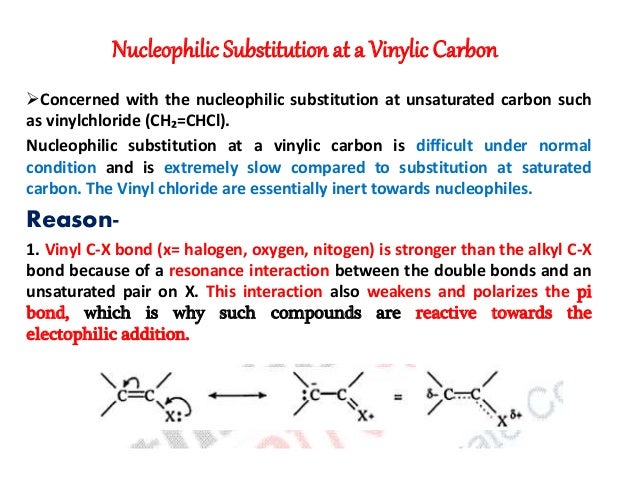
In the given compound carbon at number 3 is known as vinylic carbon because it is bonded to double bonded carbon atom. This molecule has four vinyl ic positions each marked with. Lewis structure of vinyl chloride a vinyl ic halide. Vinylic synonyms vinylic pronunciation vinylic translation english dictionary definition of vinylic.
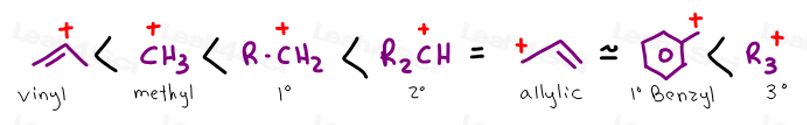
The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon. Its empirical formula is c 2 h 3 more generally a vinylic cation is any disubstituted trivalent carbon where the carbon bearing the positive charge is part of a double bond and is sp hybridized in the chemical literature substituted vinylic cations are often referred to as vinyl cations and understood to. On a carbon skeleton sp 2 hybridized carbons or positions are often called vinylic. On or bonded to the carbon of an alkene.
The univalent hydrocarbon group ch2 ch derived from ethylene. Atoms or groups attached to an allylic carbon are termed allylic substituents. Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule. They are subdivided into alkyl vinylic aryl and acyl halides.