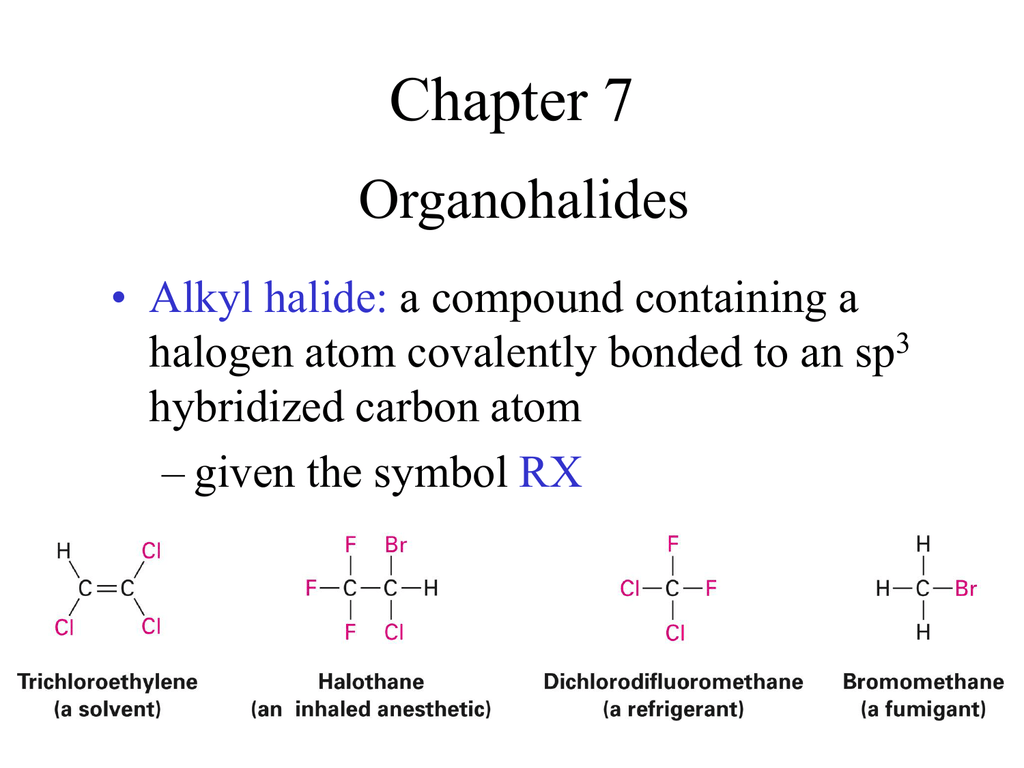
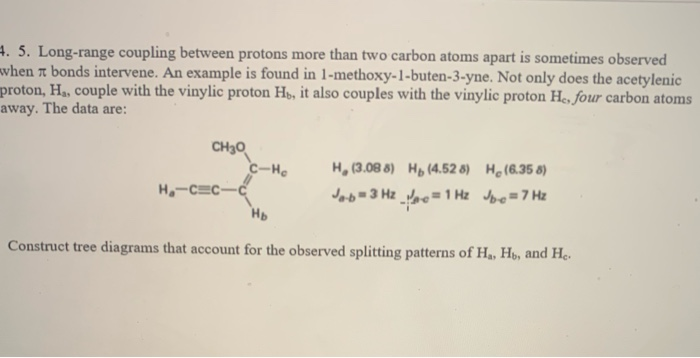
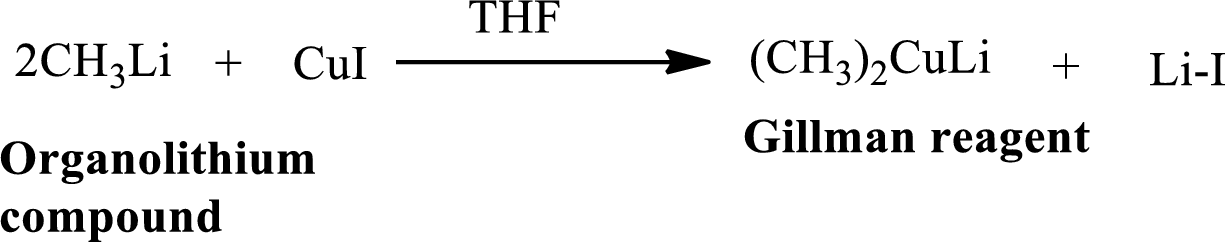
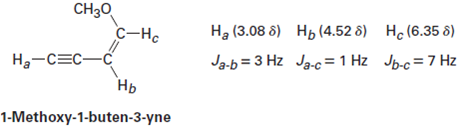Vinylic Carbon Atom

In chemistry vinyl or ethenyl abbreviated as vi is the functional group with the formula c h ch 2 it is the ethylene iupac ethene molecule h 2 c ch 2 with one fewer hydrogen atom.
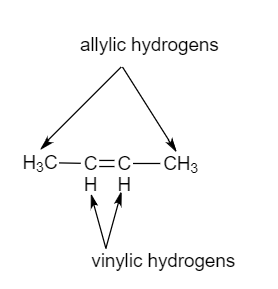
Vinylic carbon atom. It contains two sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms and one sp 3 hybridized carbon atom. Unlike vinyl group the allylic carbon atom is sp 3 hybridized as it bonded with ch ch 2 through a single covalent bond. It would be kept mentioned that allyl is the latin word that is used for the garlic allium sativum. General vinylic carbocation structure.
Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule. The allylic carbon is bonded to a carbon atom which is doubly bonded to another carbon atom. Allyl have two sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms and one sp 3 hybridized carbon atom. A phenyl carbon is the aromatic carbon that is directly connected to something outside of the ring.
Allyl form a stable carbocation because of the electron delocalization whereas vinylic carbocations are unstable as they lack p character. The name is also used for any compound containing that group namely r ch ch 2 where r is any other group of atoms. The general formula for allyl is r ch 2 ch ch 2 in which the asterisk carbon atom is an allylic carbon atom. A carbocation in which the carbon atom having the open octet and positive formal charge is part of a carbon carbon double bond.
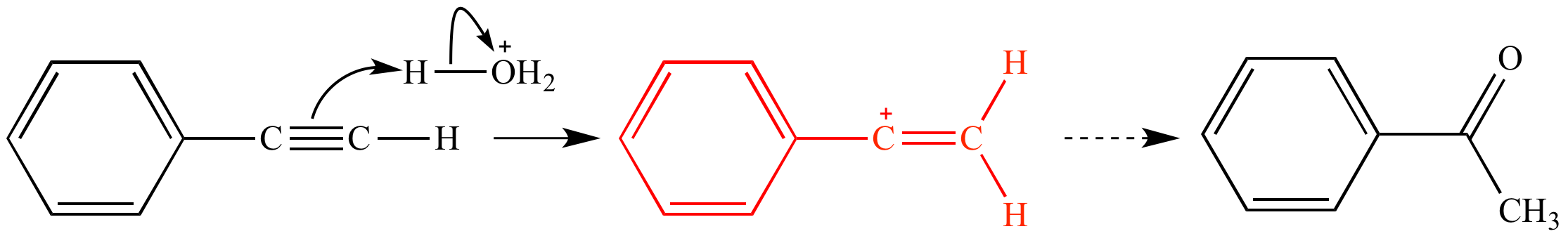
The vinyl cation is a carbocation with the positive charge on an alkene carbon. An industrially important example is vinyl chloride precursor to pvc a plastic. A phenyl group is a benzene ring directly attached to something else like a carbon. Mechanism of methyleneaziridine formation by sodium amide induced ring closure revisited.
It is the saturated carbon next to a benzene ring. In other words it is a methylene bridge ch 2 attached to a vinyl group ch ch 2. A benzylic carbon is simply the saturated carbon while a benzyl group is a benzene ring attached to something else one more carbon away. The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon.
When one hydrogen atom is removed from the third carbon atom of a propane molecule it is equivalent to an allyl group. Rare example of nucleophilic substitution at vinylic carbon with inversion. The vinyl carbocation a primary. A vinylic carbocation which has an empirical formula of c h is a carbocation that has a positive charge only on the alkene carbon atom.
Any trivalent disubstituted carbon is generally a vinylic carbocation in which the carbon atom which is bearing the positive charge is found to be double bonded and will always exist as sp hybridized.