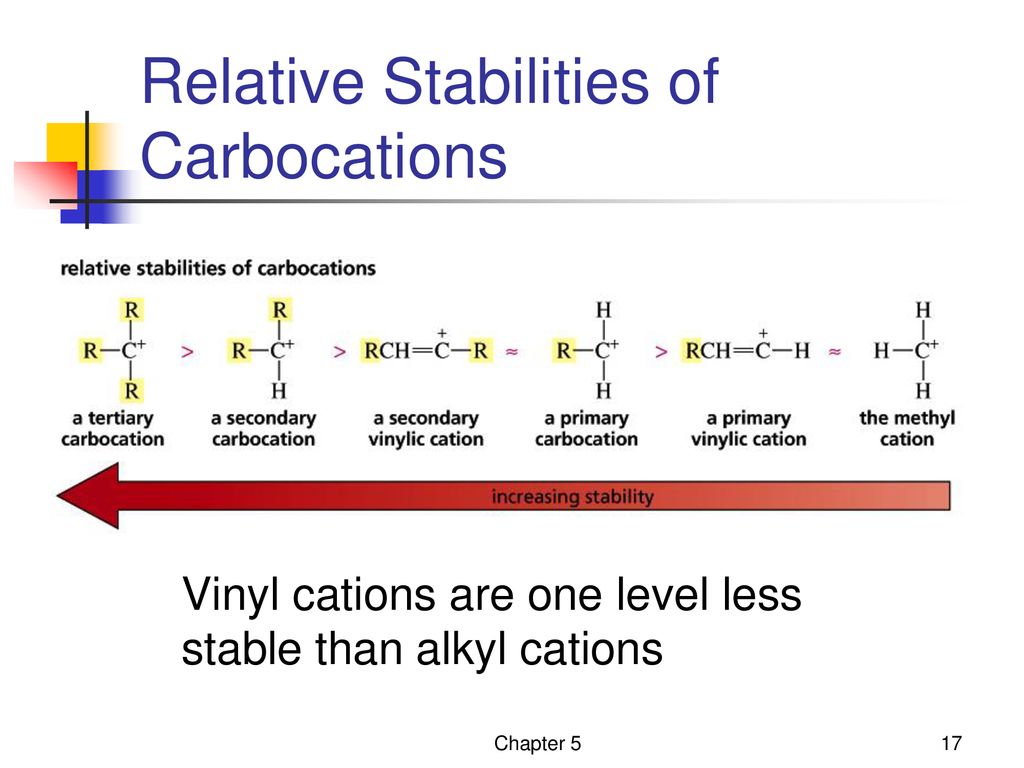
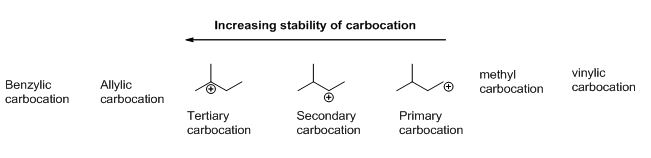
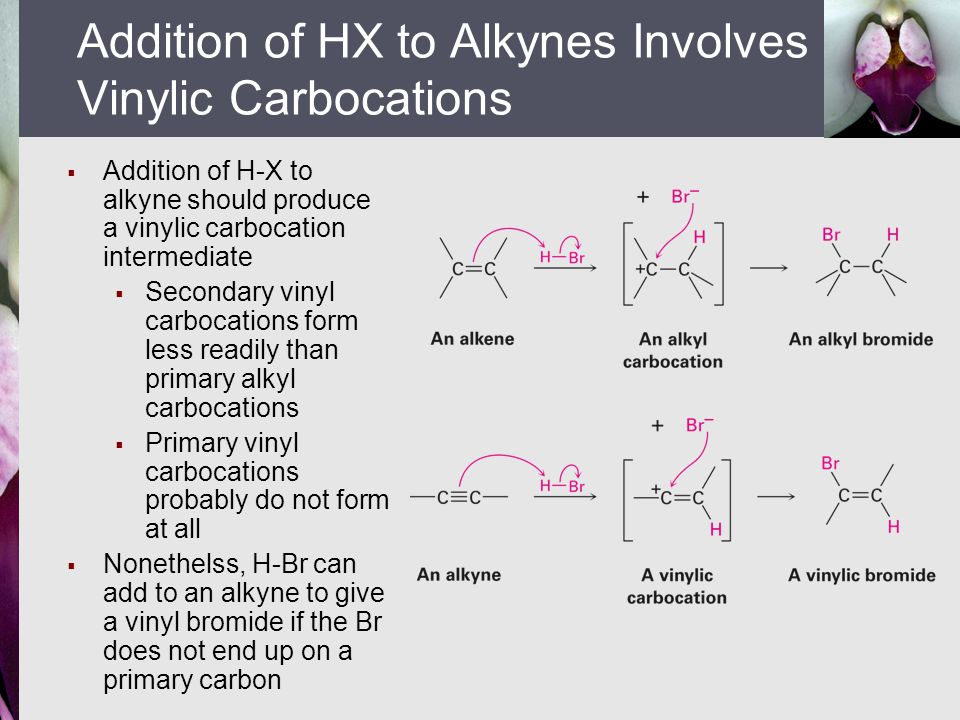
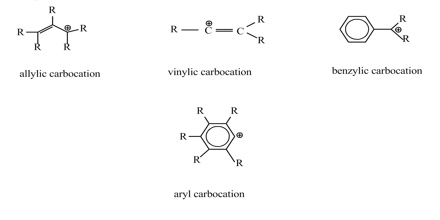
Vinylic Carbocation Stability
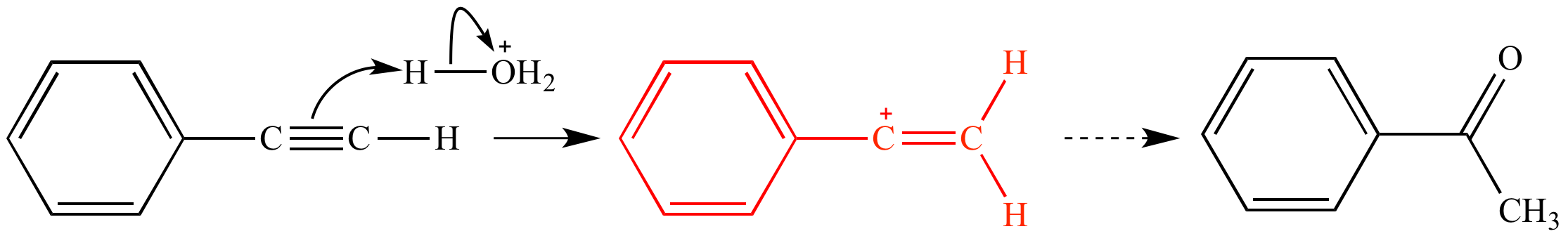
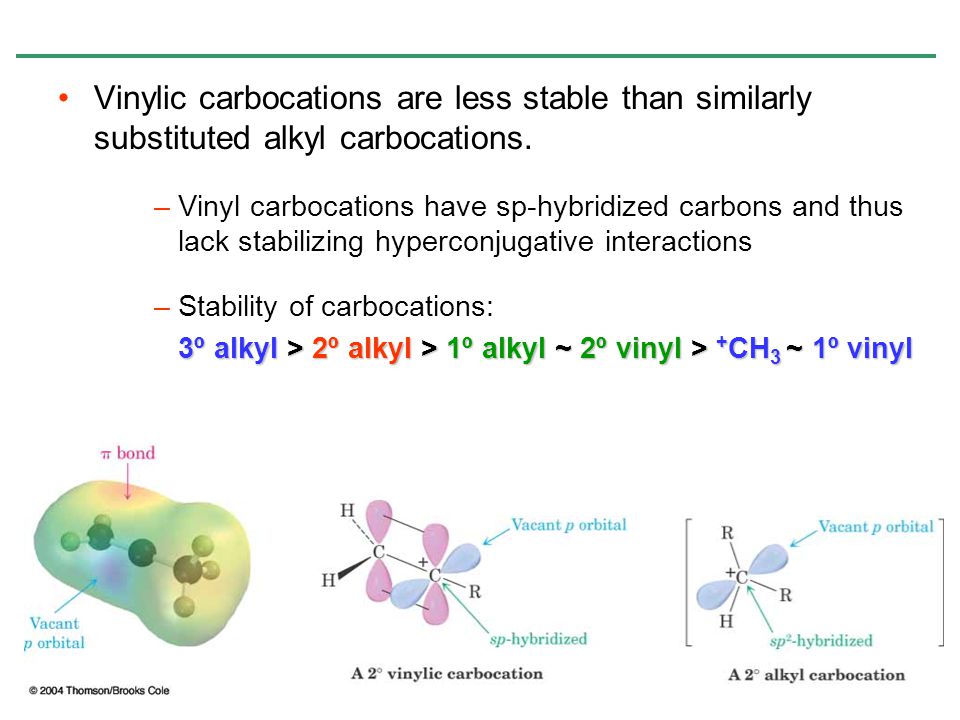
Vinyl and aryl carbocations are very rare to find due to their low stability.
Vinylic carbocation stability. We know that the rate limiting step of an s n 1 reaction is the first step formation of the this carbocation intermediate. It is therefore important to get acquainted with its characteristics. Stability of carbocation intermediates. Carbocation stability resonance rearrangement allylic vinylic examples organic chemistry duration.
This is very very unstable and ranks under a methyl carbocation in stability. Do not confuse an allylic group with a vinyl group. The rate of this step and therefore the rate of the overall substitution reaction depends on the activation energy for the process in which the bond between the carbon and the leaving group breaks and a carbocation forms. Vinylic carbocations are not able to undergo resonance.
Due to this reason the stability of a primary vinylic carbocation is less than a primary alkyl carbocation. An allylic carbocation in which an allylic carbon bears the positive charge. An allylic carbon is an sp3 carbon that is adjacent to a vinylic carbon. Table of contents formation of the carbocation carbocations carbocation stability carbocations often occur as intermediates in reactions in organic chemistry.
Atoms or groups attached to an allylic carbon are termed allylic substituents. A vinylic carbocation is a positively charged carbon that is attached to a non carbon and participates in a double bond with another carbon. How does the stability of a carbocation work. The organic chemistry tutor 100 569 views 15 37.
This will help you master carbocation intermediate reactions down the line including markovnikov alkene addition reactions unimolecular substitution sn1 β. Any trivalent disubstituted carbon is generally a vinylic carbocation in which the carbon atom which is bearing the positive charge is found to be double bonded and will always exist as sp hybridized. Allylic carbocations are able to share their burden of charge with a nearby group through resonance. In the same way lower stability of aryl carbocation in comparison to a secondary alkyl carbocation can be explained.
A vinylic carbocation which has an empirical formula of c h is a carbocation that has a positive charge only on the alkene carbon atom.