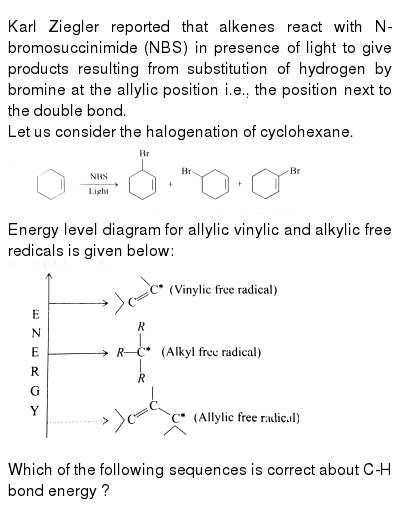
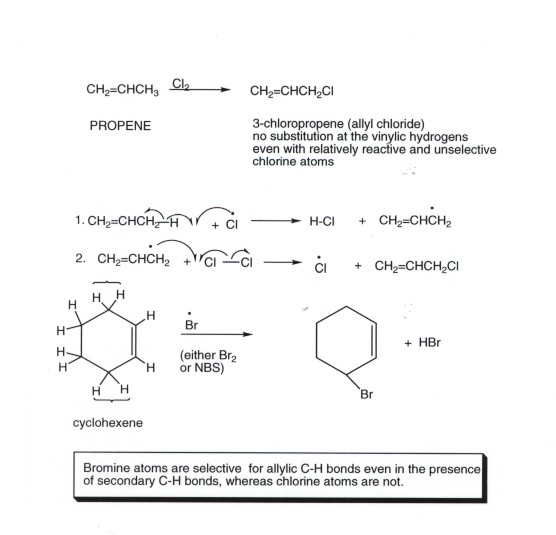
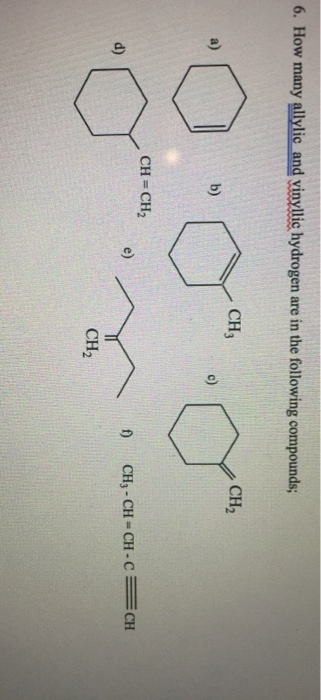
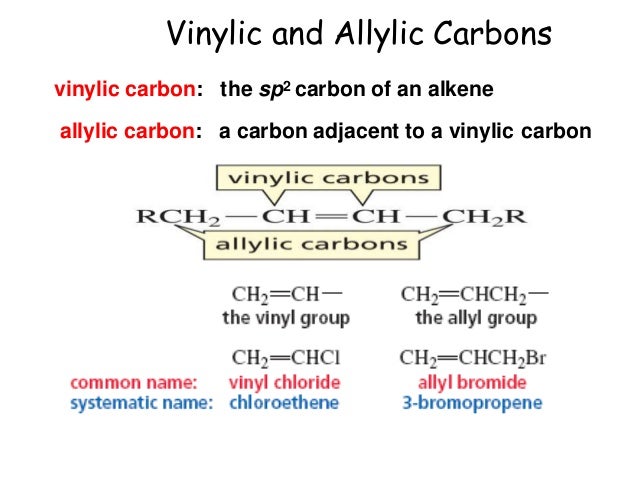
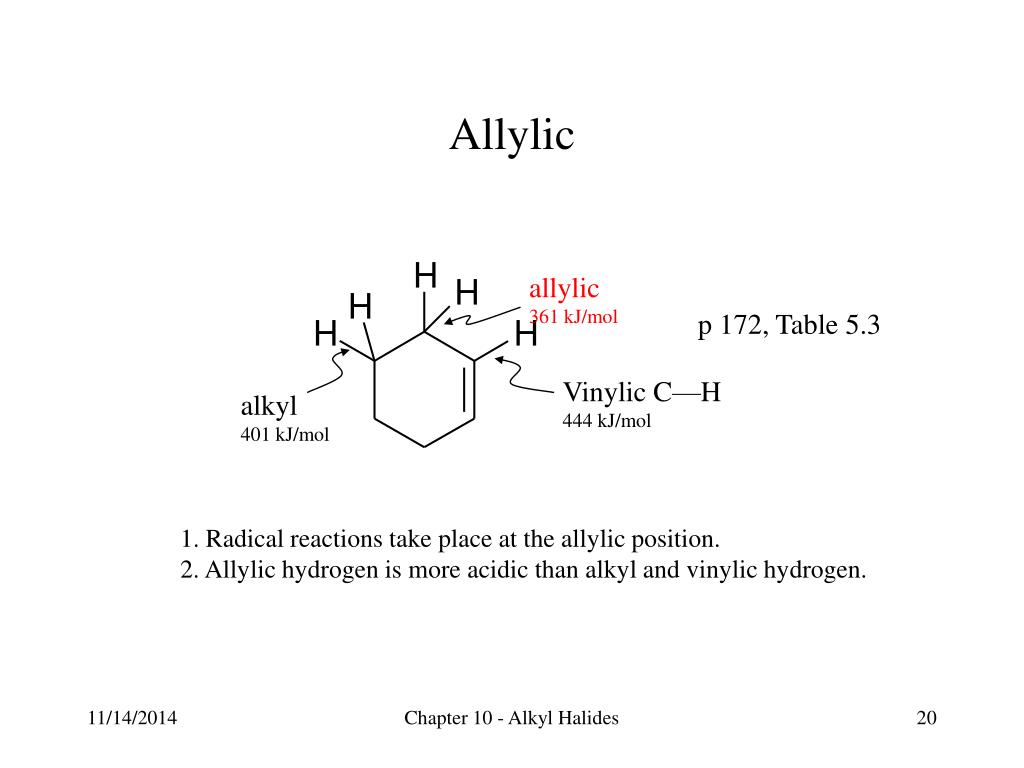
Vinylic And Allylic Hydrogens
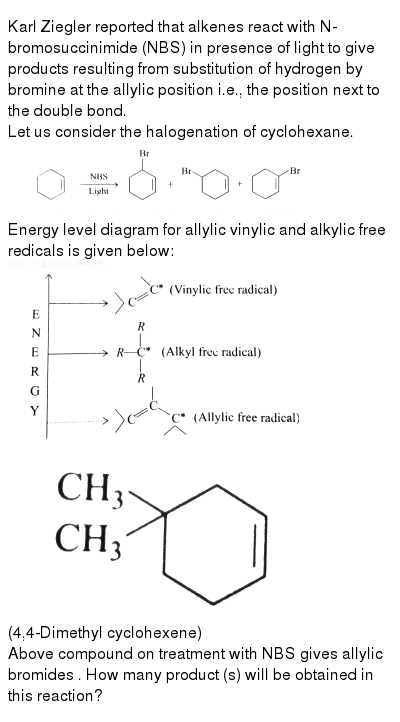
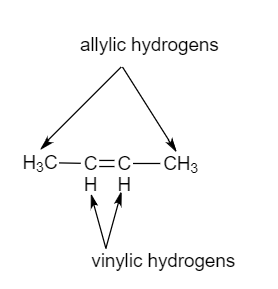
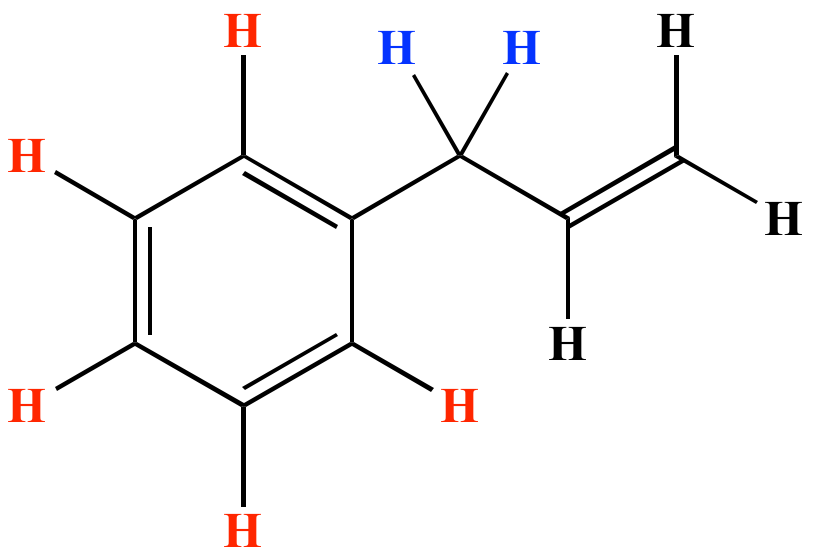
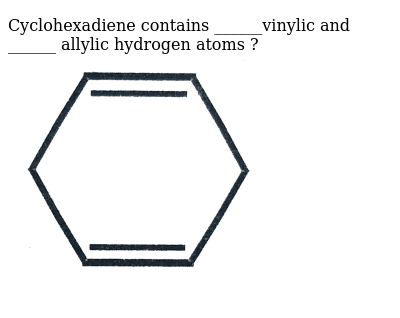
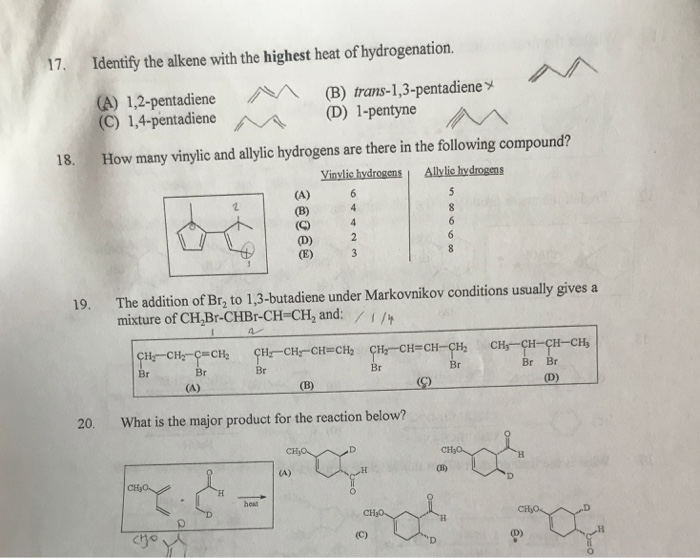
Identify the number of allylic and vinylic hydrogens in the pictured molecules.
Vinylic and allylic hydrogens. The vinylic hydrogens are shown in red. The organic chemistry tutor 93 912 views. It contains two sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms and one sp 3 hybridized carbon atom. Can you draw the structure.
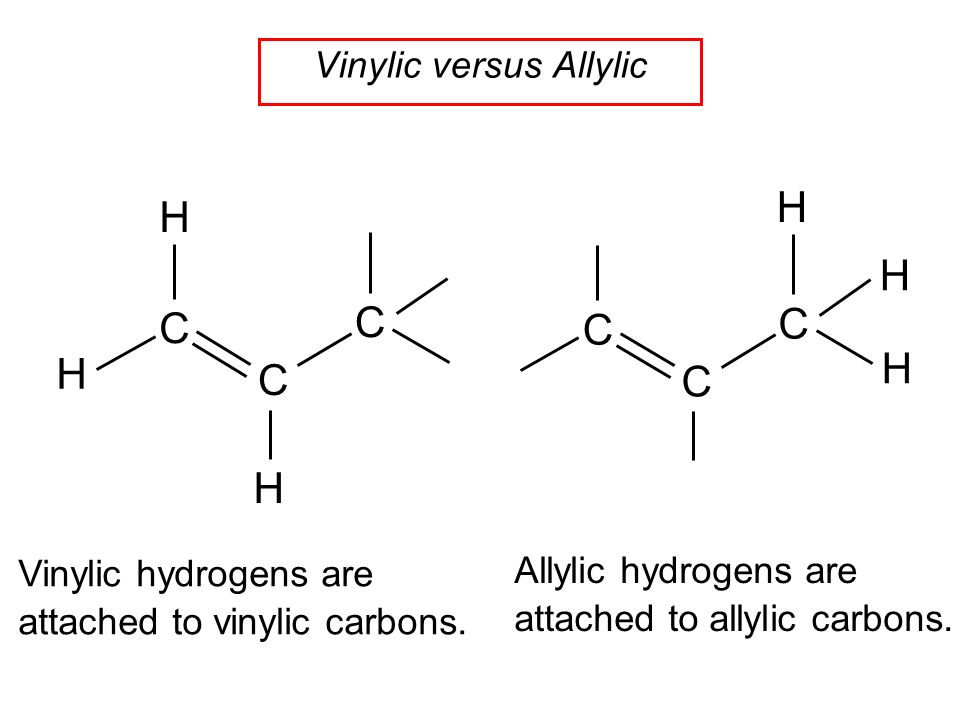
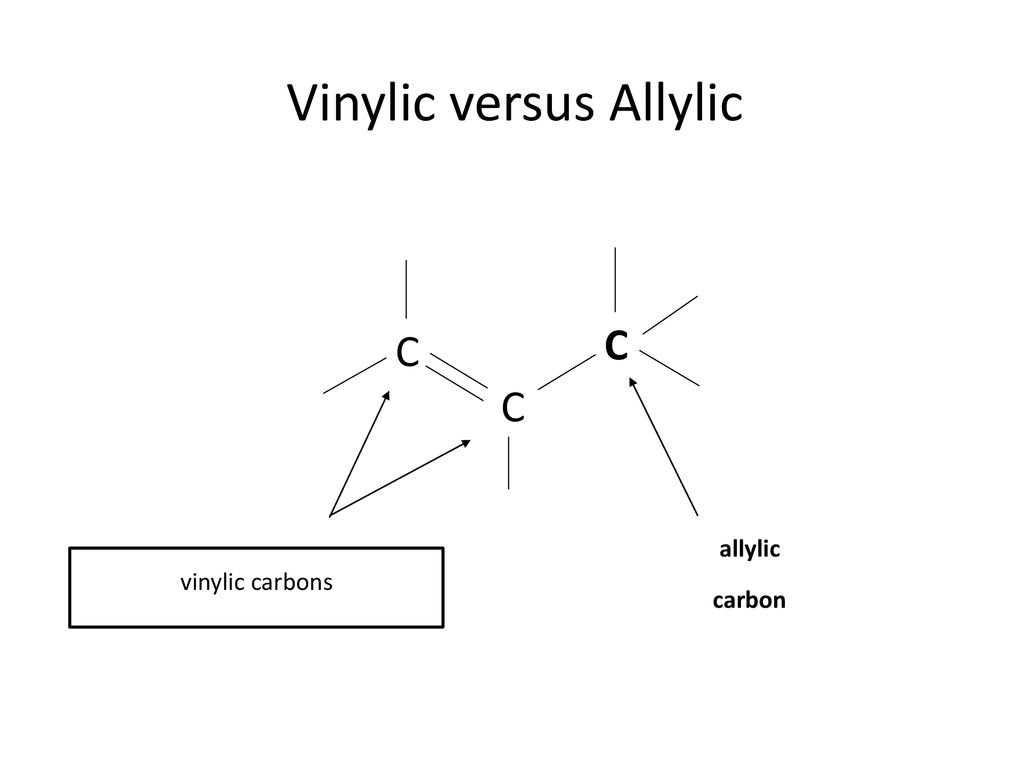
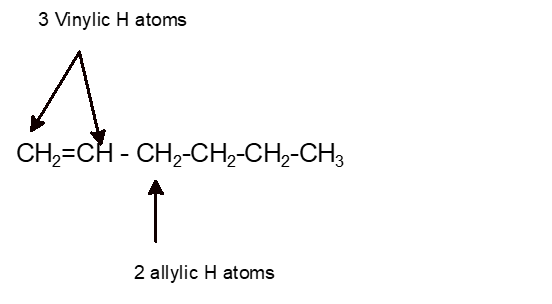
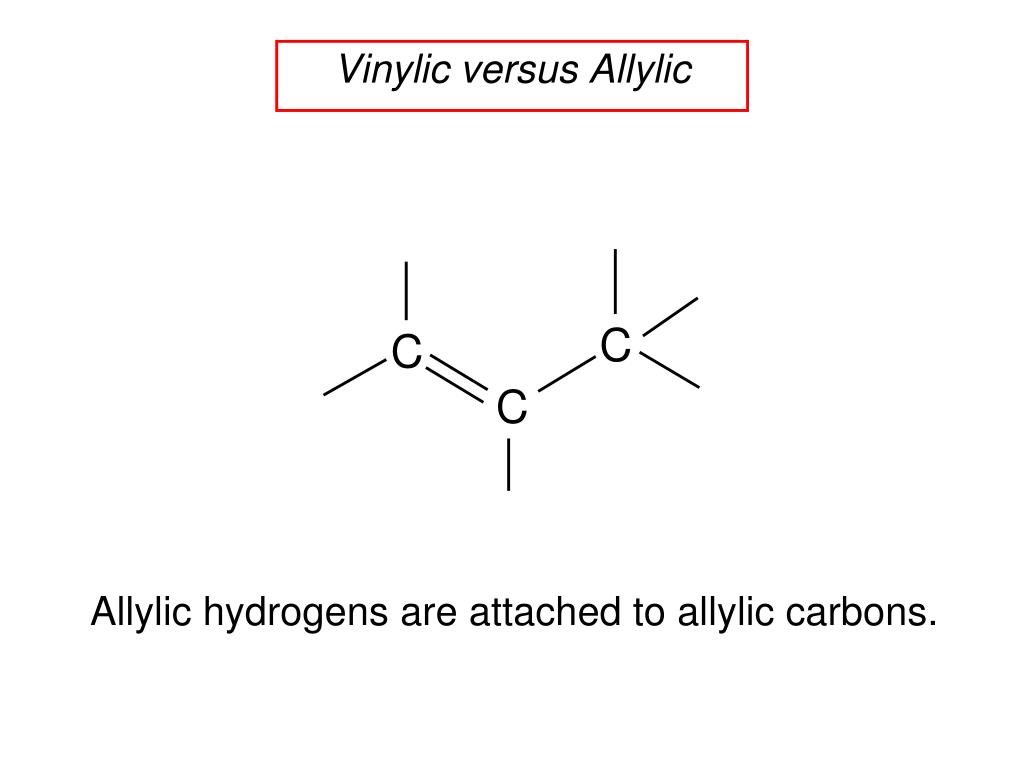
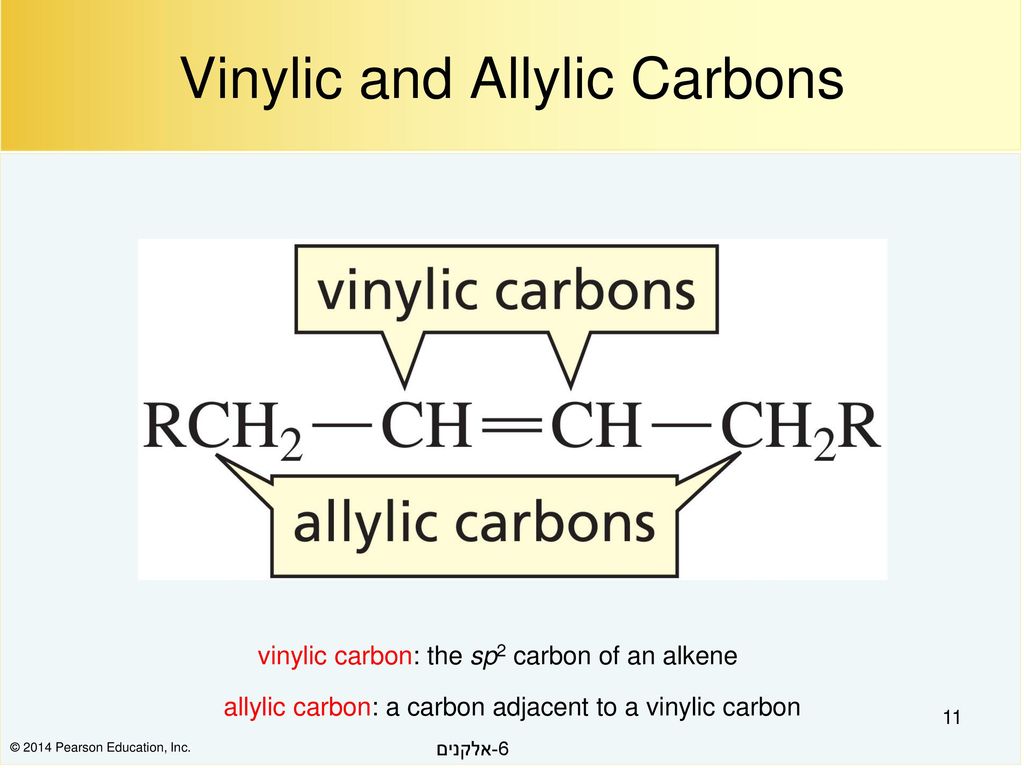
The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon. A hydrogen atom bonded to an sp 2 carbon of an alkene. Allyl indicates a functional group with structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule it consists of methylene bridge ch 2 in between the vinyl group ch ch 2 and the rest of the molecule therefore allyl group contains sp 2 hybridized vinyl carbon atoms and sp 3 hybridized allyl carbon atom. How many vinylic hydrogens are there in 1 ethylcyclohexene.
The allylic carbon atom is more reactive than normal. When one hydrogen atom is removed from the third carbon atom of a propane molecule it is equivalent to an allyl group. Identify the number of allylic and vinylic hydrogens in the pictured molecules. In other words it is a methylene bridge ch 2 attached to a vinyl group ch ch 2.
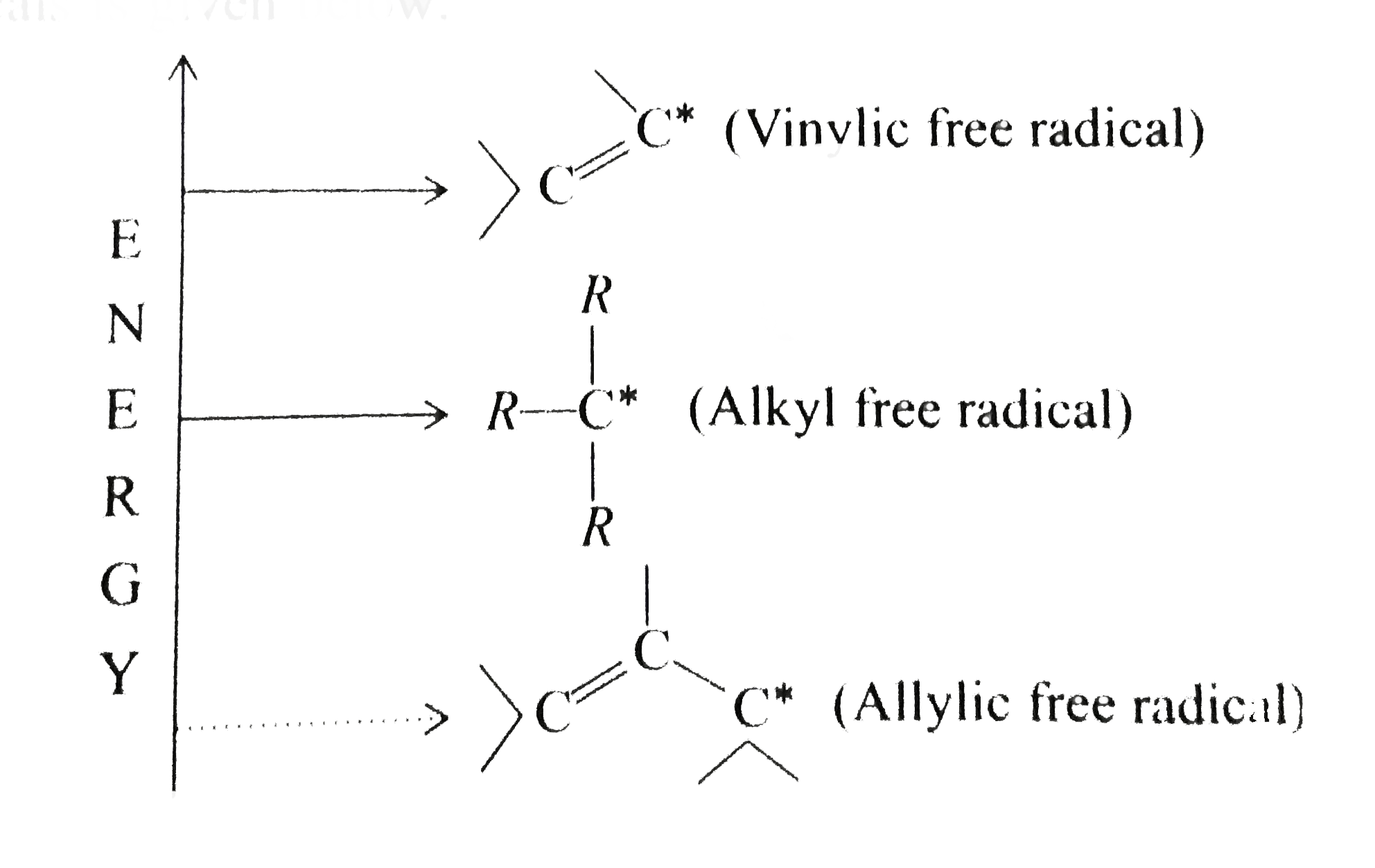
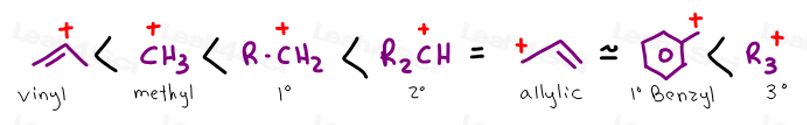
Atoms or groups attached to an allylic carbon are termed allylic substituents. An allylic carbon is an sp3 carbon that is adjacent to a vinylic carbon. Allyl form a stable carbocation because of the electron delocalization whereas vinylic carbocations are unstable as they lack p character. How many types of allylic hydrogens are there in 1 ethylcyclohexene.
An allylic carbocation in which an allylic carbon bears the positive charge. An allylic hydrogen is a hydrogen atom that is bonded to an allylic carbon in an organic molecule. None of the other hydrogens are vinylic. Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule.